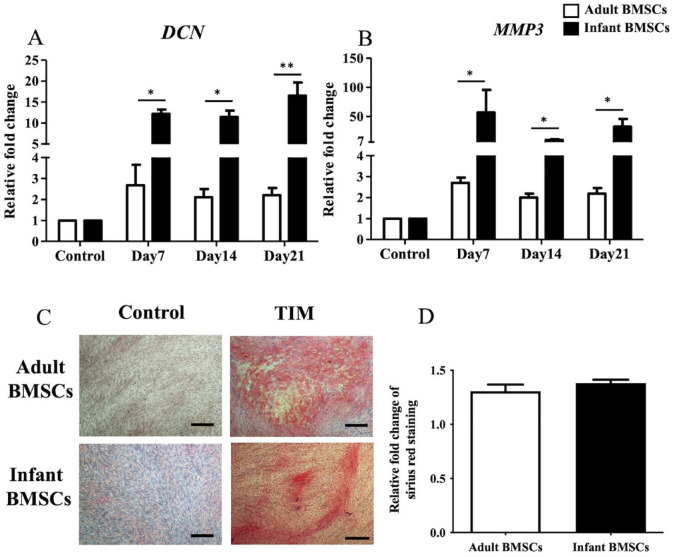
Figure 7.
Detection of tendon-related gene expressions of adult and infant BMSCs during differentiation using TIM. (A) The expression of DCN and (B) MMP3 genes in adult and infant BMSCs during tenogenic differentiation from days 7 to 21 was detected using RT-qPCR. The expression values of each gene were normalized to the expression of GAPDH. Undifferentiated cells were used as a control to compare the gene expression of adult and infant BMSCs after differentiation, showing the relative fold change. (C) Undifferentiated adult and infant BMSCs were stained with Picro-Sirius Red as a control. The 21-day tenogenic differentiated adult and infant BMSCs were confirmed using Picro-Sirius Red staining and observed under a Nikon eclipse TS100 microscope (magnification × 40, scale bar = 50 μm). (D) The Picro-Sirius Red stain was extracted from the stained cells, and the optical density (OD) was measured at a wavelength of 550 nm. Subsequently, the OD values of the differentiated cells were normalized against the control values set as 1 (not shown in the figure), presenting the relative fold changes compared with the control. The mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) calculated from three experimental replicates within both the infant and adult groups. Statistical significance in the comparison of tenogenic differentiation between adult and infant BMSCs was determined using the Mann–Whitney U test. BMSC: bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cell; DCN: decorin; MMP3: matrix metallopeptidase 3; TIM: tenogenic induction medium; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; RT-qPCR: real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Significance levels are indicated by *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.