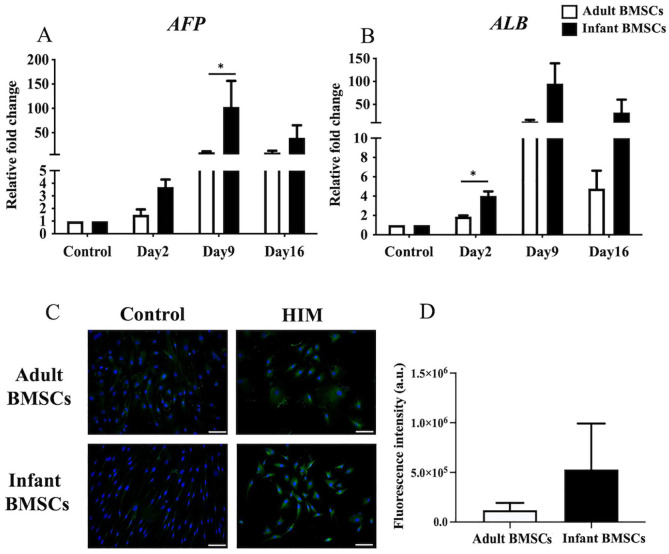
Figure 9.
Detection of hepatocyte-related gene expressions of adult and infant BMSCs during differentiation using HIM. (A) The expression of AFP and (B) matrix ALB genes in adult and infant BMSCs after 13-15 days of factor-induced hepatogenic differentiation was detected using RT-qPCR. The expression values of each gene were normalized to the expression of GAPDH. Undifferentiated cells were used as a control to compare the gene expression of adult and infant BMSCs after differentiation, showing the relative fold change. (C) The presence of albumin protein in adult and infant BMSCs was detected using immunofluorescence staining, represented by green fluorescence, and evaluated using an Olympus BX43 microscope. Nuclear DNA stained by DAPI is shown in blue fluorescence. (Magnification × 400, scale bar = 100 μm). (D) Immunofluorescence intensity was quantified using ImageJ. The mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) calculated from three experimental replicates within both the infant and adult groups. Undifferentiated adult and infant BMSCs were stained with DAPI and antibody, establishing the control set at 1 (not shown in the figure), demonstrating the relative fold changes of differentiated cells compared with the control. Statistical significance of comparing adult and infant BMSCs in hepatogenic differentiation was determined using the Mann–Whitney U test. BMSC: bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cell; AFP: alpha-fetoprotein; ALB: albumin; HIM: hepatogenic induction medium; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; RT-qPCR: real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Significance levels are indicated by *P < 0.05.