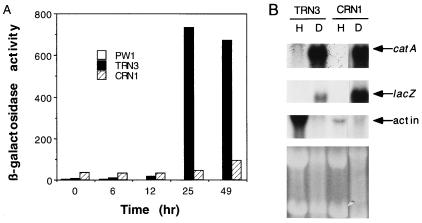
FIG. 3.
Expression of catA and catA::lacZ reporter fusion in wild-type and brlA mutant strains during conidiation. (A) Plasmid pREN8, containing catA gene upstream sequences extending from the fourth proposed codon fused to the E. coli lacZ gene, was integrated at argB by transformation of the developmentally wild-type strain PW1. Transformant TRN3, containing a single copy of pREN8 integrated at argB, was crossed to brlA17 mutant strain CRN10 to produce the brlA17 mutant strain CRN1, containing the catA::lacZ fusion (Table 1). Both strains were grown in liquid medium for 18 h and induced to conidiate. Water-soluble protein extracts were prepared from samples harvested at the indicated times and assayed for β-galactosidase specific activity (24). The different times of development correspond to the following morphologies: 0 h of development (18 h of growth), undifferentiated hyphae; 6 h, conidiophore stalks; 12 h, conidiophores and first immature conidia; 25 h, mature conidiophores and conidia. β-Galactosidase activity in isolated conidia corresponded to 9,430 U. β-Galactosidase activities corresponding to strains TRN3 and CRN1 shown here and those indicated in the text are mean values from two independent experiments, with a maximum variation of 21% with respect to the mean. (B) Total RNA extracted from growing hyphae (H; 18 h of growth) or developmental cultures (D; 49 h of conidiation) was fractionated in formaldehyde-agarose gels, transferred to a nylon membrane, and hybridized to catA-, lacZ-, and actin-specific probes. The bottom part shows rRNA bands in the ethidium bromide-stained gel used to prepare the blot.