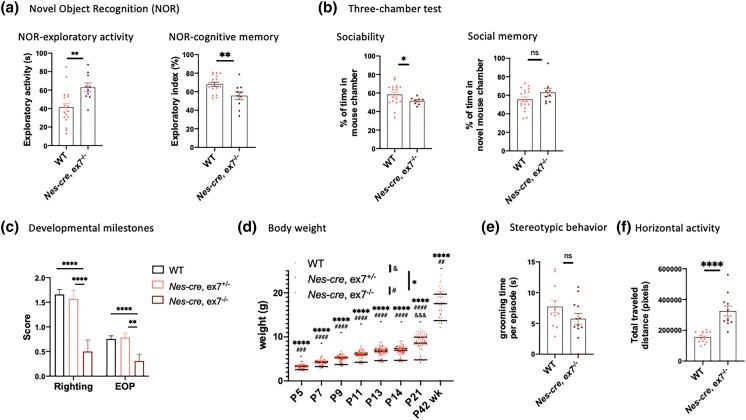
Fig. 5.
Developmental and behavioral characterization of Nes-cre, ex7−/− mutants. a) Novel object recognition test showed that Nes-cre, ex7−/− animals displayed increased exploratory activity (left panel) and impaired cognitive memory (right panel) compared to WT animals. N = 10–18 animals for each genotype. b) Three-chamber test (see Methods) showed that Nes-cre, ex7−/− animals displayed decreased sociability (left panel) but normal social memory (right panel) compared to WT animals. N = 9–18 animals for each genotype. One outlier was excluded from Nes-cre, ex7−/− group through Grubb's test for both sociability and social memory measurements, with G = 2.543 and 2.372, respectively, at alpha = 0.05. c) Developmental delay tests of righting reflex and eye-opening (EOP) scores (see Methods). Nes-cre, ex7−/− mice showed significantly reduced scores in both righting reflex and EOP tests compared to WT mice and Nes-cre, ex7−/+ animals, but not Nes-cre, ex7−/+ to WT mice. WT N = 44–45; Nes-cre, ex7−/+ N = 21–24; Nes-cre, ex7−/− N = 14. d) Body weight measurements at different developmental time points. P5-adult (P42–P49) animals were measured for body weight. WT N = 14–47; Nes-cre, ex7−/+ N = 6–25; Nes-cre, ex7−/− N = 10–14; & = statistical significance between WT and Nes-cre, ex7−/+ comparisons, #statistical significance between Nes-cre, ex7−/+ and Nes-cre, ex7−/− comparisons; *statistical significance between WT and Nes-cre, ex7−/− comparisons. e) Stereotypic behavior was measured with grooming time per episode and not significantly different in WT and Nes-cre, ex7−/− animals. N = 12 for each genotype. f) Horizontal activity was significantly increased in Nes-cre, ex7−/− animals compared to WT controls. N = 11–15 for each genotype. Two-tailed unpaired t-test was used to test statistical significance, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ns= not significant.