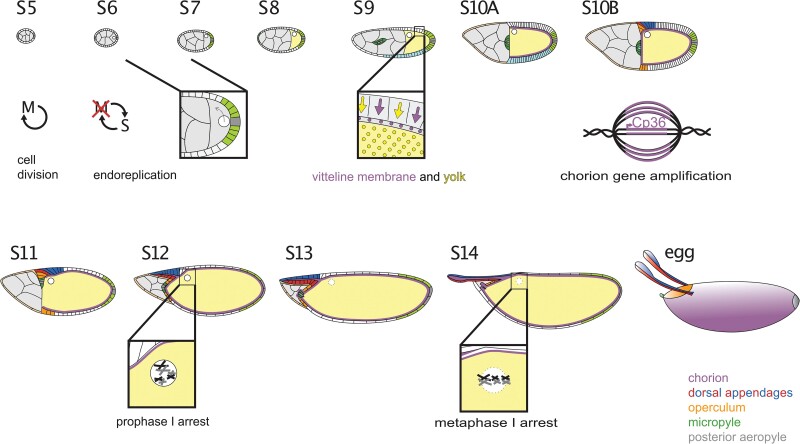
Fig. 2.
Stages of oogenesis. Germline cysts enveloped by a follicular epithelium emerge from the germarium as S1 egg chambers. This chapter focuses on the events from S5 onward that are needed to finish the egg. At S5, the follicle cells complete their last mitotic cycle and enter an endoreplication cycle at S6. They shut down endocycling at the transition from S10A to 10B, but they continue to amplify regions encoding the chorion genes. At S6, a signal from posterior follicle cells induces a reorganization of the oocyte cytoskeleton, and the oocyte nucleus moves to the anterior. From S8 to S10, the follicle cells synthesize and secrete yolk proteins and vitelline membrane proteins, and from S10 to S14, they synthesize and secrete the layers and specializations of the eggshell. At S9, the border cells delaminate and migrate between the nurse cells while the stretch cells flatten. At S10B, the centripetal cells begin to ingress. At S11, the nurse cells transfer their contents into the oocyte and begin to break down; at the same time, the dorsal appendage cells wrap to make 2 tubes. From S1 to S12, the oocyte chromosomes are held in a prophase I arrest. At S13, the oocyte nuclear envelope breaks down and the chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate. When the egg chamber moves into the oviduct, the follicle cells and nurse cell remnants slough off, revealing the eggshell.