Figure 1.
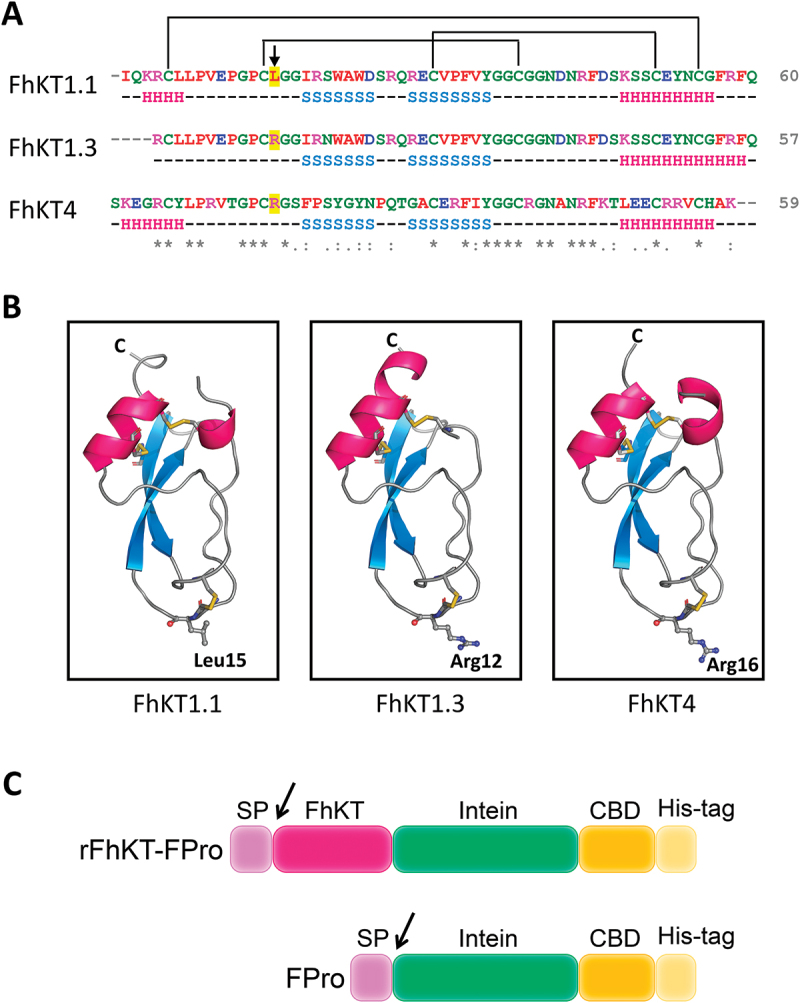
Amino acid sequence alignment and modelling of FhKT proteins (a) alignment sequence of amino acids of members belonging to the family of Kunitz type inhibitors of F. hepatica. Conserved amino acids are indicated by an asterisk (*), strong amino acid group similarity by a colon, and weaker group similarity by a single dot. The colour code indicates the different types of amino acids according to clustal omega. The P1 residue within the reactive site loop is indicated with an arrow. Predicted secondary structure (H = helix, S = strand) is shown below the sequences. Above the sequence, the disulphide bridge pattern is drawn. The lines connecting the cysteine residues represent the disulphide bonds. (b) ribbon representation of FhKT1.1, FhKT1.3 and FhKT4 structures predicted by AlphaFold2. P1 site residues are shown as ball-and-stick and disulphide bonds as yellow sticks. Ribbon representation of FhKT1.1, FhKT1.3 and FhKT4 secondary structures predicted by AlphaFold2. The three disulphide bonds (yellow), an alfa-helix (pink), and anti-parallel beta-sheets (blue) are shown. (c) schemes of the fusion proteins. The N-terminal pET26 pelB SP (signal peptide, 2.23 kDa), the FhKT of interest (F. hepatica KT-like protein, FhKT1.1: 6.79 kDa, or FhKT1.3: 6.49 kDa or FhKT4: 6.65 kDa), and the C-terminal intein (Ssp DNAx intein, 15.44 kDa), CBD (chitin binding domain, 6.61 kDa) and His-tag (poly histidine affinity tag, 1.44 kDa), are indicated. FPro corresponds to the fusion protein (intein-CBD-Histag).
