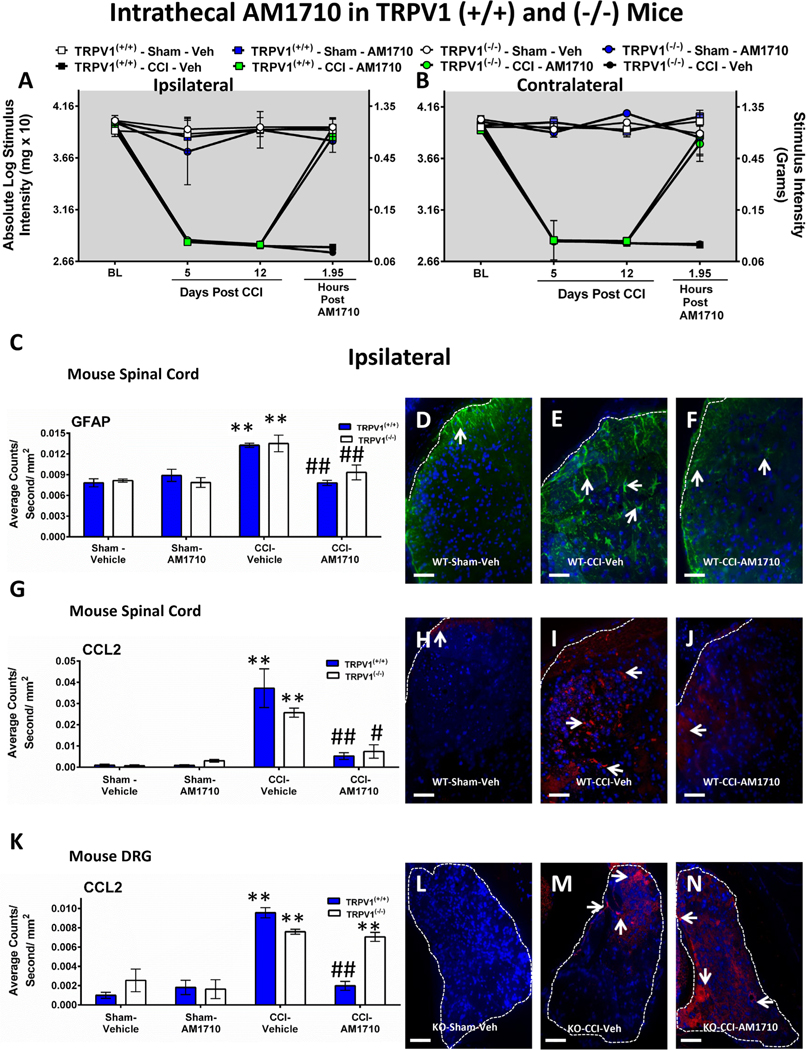
Fig. 2.
Intrathecal (i.t.) AM1710 reverses CCI-induced allodynia and modulates spinal GFAP, CCL2 in wild type and globally deleted TRPV1 knockout mice. A, B, AM1710 reverses CCI-induced allodynia independently of spinal TRPV1 actions. Unilateral CCI surgery produced significant bilateral allodynia in both TRPV1(+/+) wildtype (WT) and (−/−) knockout (KO) mice at Day 5 and 12 following unilateral injury. AM1710 (5 μg) maximally reversed CCI-induced allodynia in both TRPV1 (+/+) and (−/−) mice at ~2 h after i.t. administration. Sections of lumbar (L4-L6) dorsal horn spinal cord and corresponding L4-L6 DRG taken from these behaviorally-verified mice were then analyzed. C, Semi-quantitative microscopy analysis of immunofluorescent immunoreactivity (IR) revealed GFAP expression in ipsilateral dorsal horn spinal cord was increased in both TRPV1(+/+) (striped bars) and TRPV1(−/−) (blue bars) CCI mice receiving i.t. vehicle compared to control sham mice given either i.t. vehicle or AM1710, while GFAP IR was significantly reduced in CCI neuropathic mice given i.t. AM1710. D, E, F, Representative spectral images at 20x magnification of GFAP IR labeling (green) with DAPI nuclear stain (blue) in ipsilateral dorsal horn spinal cord. White dashed lines indicate the border between spinal cord and intrathecal space. G, Irrespective of TRPV1 genetic background, compared to sham controls, CCL2 expression was increased in the ipsilateral dorsal horn spinal cord of CCI mice given i.t. vehicle. However, i.t. AM1710 in CCI mice robustly suppressed CCL2 IR. H, I, J, Representative spectral images at 20x magnification of CCL2 IR labeling (red) with DAPI nuclear stain (blue) in ipsilateral dorsal horn spinal cord. White dashed lines indicate the border between spinal cord and intrathecal space. K, Ipsilateral lumbar DRG demonstrate increased CCL2 expression from CCI mice that received i.t. vehicle compared to control sham mice. While CCL2 IR was decreased to sham levels in TRPV1(+/+) (striped bars), CCI mice given i.t. AM1710, TRPV1 (−/−) mice (blue bars) displayed continued elevated CCL2 IR in ipsilateral DRG. L, M, N, Representative spectral images at 20x magnification of CCL2 fluorescent labeling (red) with DAPI nuclear stain (blue) in ipsilateral DRG. The border around the DRG is indicated by white dashed lines. In all images the scale bar is equal to 50 μm. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 vs. Sham Vehicle-injected control, ##p < 0.01, #p < 0.05 vs. CCI Vehicle-injected control (Tukey’s test), and results are mean ± S.E.M., n = 5–6 mice/group.