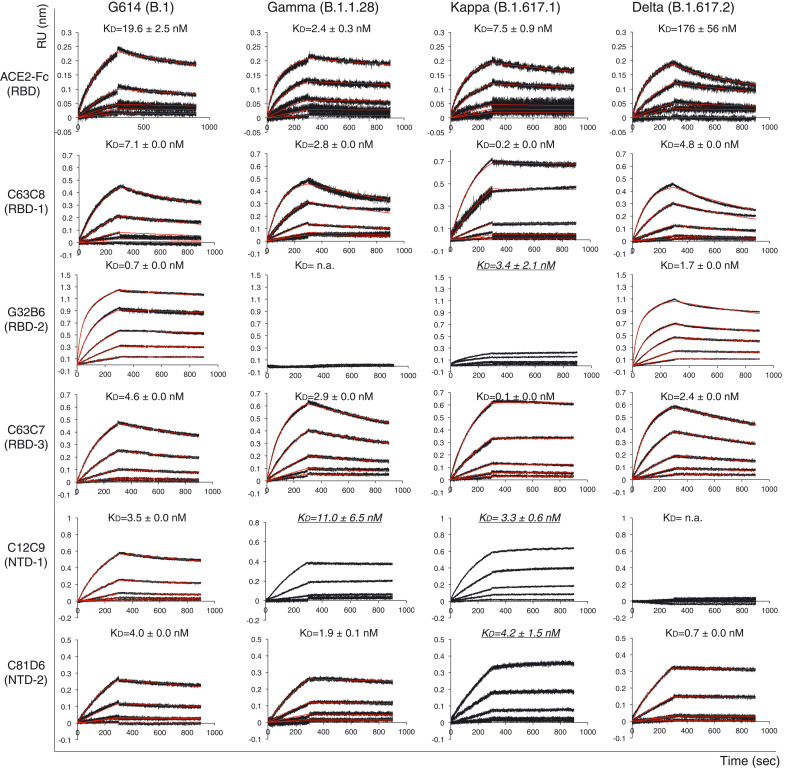
Fig. 2. Antigenic properties of purified full-length SARS-CoV-2 S proteins.
Biolayer interferometry (BLI) analysis of the association of prefusion S trimers derived from the G614 “parent” strain (B.1) and the Gamma (B.1.1.28), Kappa (B.1.617.1), and Delta (B.1.617.2) variants with soluble ACE2 constructs and with a panel of antibodies representing five epitopic regions on the RBD and NTD (see fig. S4A) (32). For ACE2 binding, purified S proteins were immobilized to AR2G biosensors and dipped into wells containing ACE2 at various concentrations. For antibody binding, various antibodies were immobilized to AHC biosensors and dipped into wells containing each purified S protein at different concentrations. Binding kinetics were evaluated by a 1:1 Langmuir model except for dimeric ACE2 and antibody G32B6 targeting the RBD-2, which were analyzed by a bivalent binding model. All KD values for multivalent interactions with antibody IgG or dimeric ACE2 and trimeric S protein are the apparent affinities with avidity effects. Sensorgrams are in black and fits are in red. Binding constants highlighted by underlines were estimated by steady state analysis as described in the materials and methods. RU, response unit. Binding constants are summarized both here and in table S1. All experiments were repeated at least twice with essentially identical results.