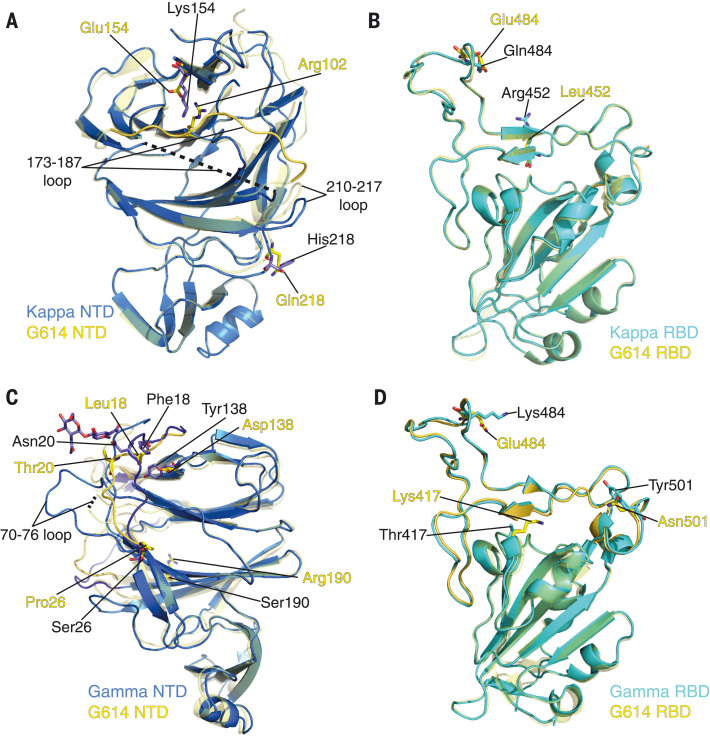
Fig. 5. Structural impact of mutations in the Kappa and Gamma S proteins.
(A) Superposition of the NTD structure of the Kappa S trimer (blue) with the NTD of the G614 S trimer (yellow). Locations of mutations E154K and Q218H, as well as Arg102 which forms a salt bridge with Glu154 in the G614 structure, are indicated; these residues are shown in the stick model. The 173 to 187 loop in the G614 trimer is highlighted in a darker color; it becomes disordered in the Kappa trimer. (B) Superposition of the RBD structure of the Kappa S trimer (cyan) with the RBD of the G614 S trimer (yellow). Locations of mutations L452R and E484Q are indicated; these residues are shown in the stick model. (C) A view of superposition of the NTD structures of the Gamma (blue) and G614 (yellow; PDB ID: 7KRR) S trimers in the one-RBD-up conformation. Locations of mutations L18F, T20N, P26S, D138Y, and R190S are indicated, as well as the N-linked glycan attached to Asn20 in the Gamma structure; these residues are shown in the stick model. (D) Superposition of the RBD structure of the Gamma S trimer (cyan) with the RBD of the G614 S trimer (yellow). Locations of mutations K417T, E484K, and N501Y are indicated, and these residues are shown in the stick model.