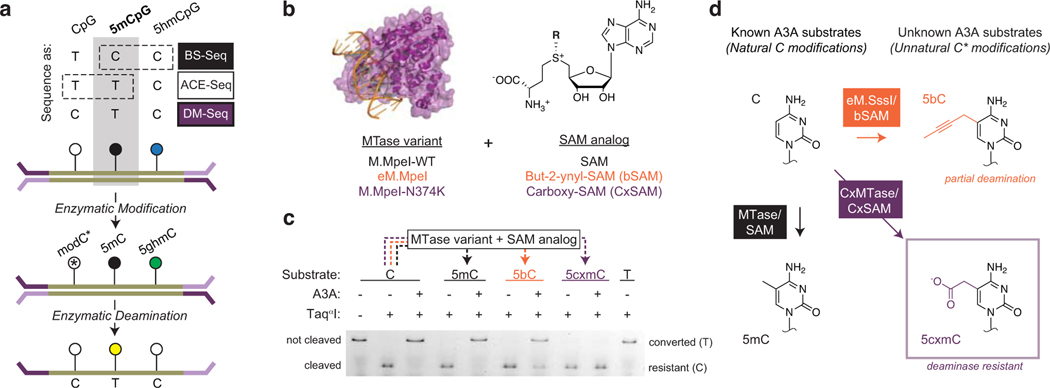
Figure 1. Direct Methylation Sequencing (DM-Seq) is enabled by 5cxmC generation.
a) Top: Sequencing methods for localizing C, 5mC, and 5hmC differ in their use of chemical (e.g. BS-Seq) or enzymatic (e.g. ACE-Seq) deamination, with 5mC signal confounded by either 5hmC or C (boxes with dashed lines). Bottom: Proposed workflow for DM-Seq. DM-Seq was envisioned as an all-enzymatic workflow for the direct detection of only 5mC. This goal could be realized by coupling an engineered DNA MTase (MTase*) with a SAM analog to create a sterically bulky cytosine base that resists deamination by APOBEC3A (A3A). C*, modified C generated from MTase and SAM analog; 5ghmC, Glucosylated 5hmC. In the proposed workflow, only 5mC alone is converted T at CpG sites. b) MTase variants and SAM analogs including two candidates for DM-Seq. c) Restriction enzyme coupled assay for assessing A3A deamination of unnatural cytosine analogs. An oligonucleotide with a single TaqαI restriction site (TCGA) is modified by the appropriate MTase variant to create 5mC, 5bC, or 5cxmC (dashed lines). Modified DNA is then deaminated by A3A. TaqαI only cleaves DNA if C is protected from A3A deamination. Experiment was performed twice with similar results. See Extended Data Fig. 2 for assay schematic and ESI-MS validation of 5bC and 5cxmC substrates. d) Summary of reactivity of various cytosine derivatives towards A3A. Left: Cytosine (C) is modified to 5-methylcytosine (5mC) by WT MTases and SAM. Both C and 5mC are favorable substrates for enzymatic deamination by A3A. Right: structures of 5-(but-2-ynyl)cytosine (5bC) and 5-carboxymethylcytosine (5cxmC), with previously uncharacterized reactivity towards A3A. Box: 5cxmC satisfies the criteria required for the DM-Seq strategy: efficient MTase* transfer and complete protection from A3A deamination.