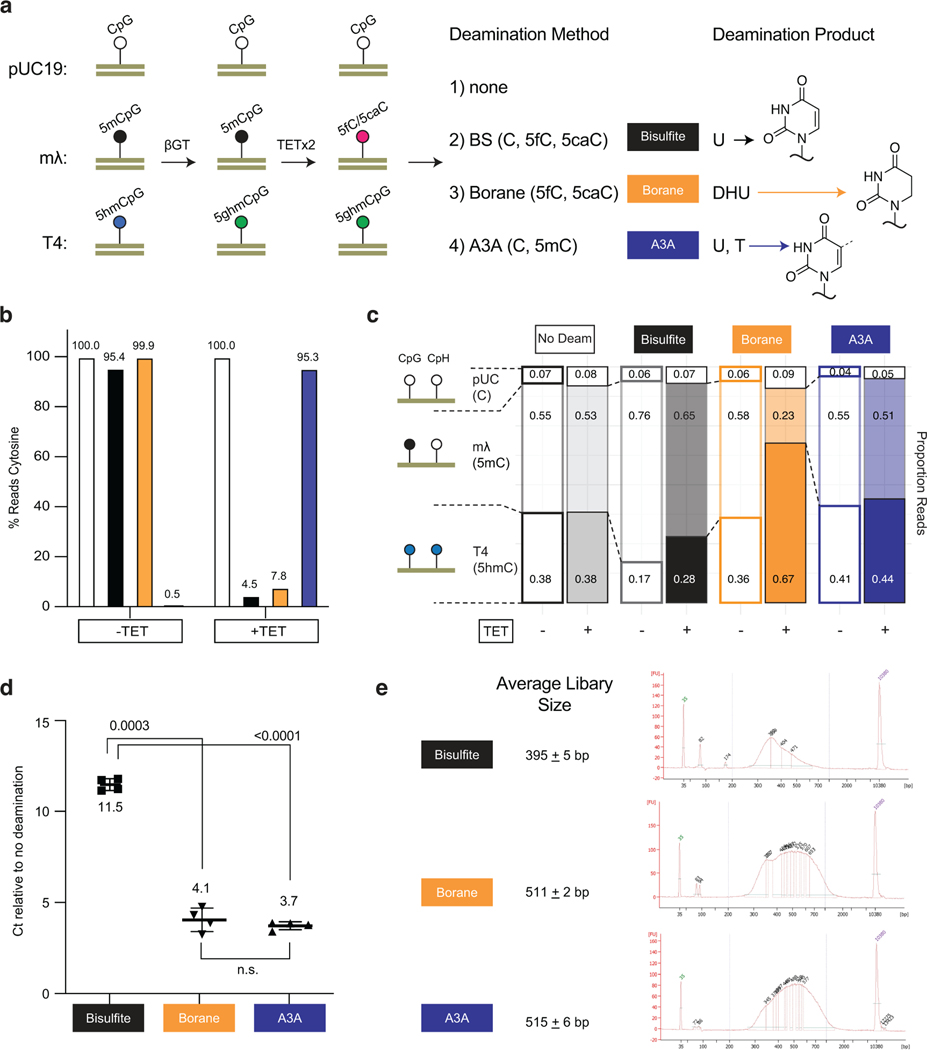
Extended Date Figure 8. Comparison of deamination methods show that TAPS bias is dependent on both TET and borane-mediated deamination.
a) Workflow for comparing deamination methods. A mixture of unmodified pUC19 DNA, 100% CpG methylated lambda phage, and T4-hmC phage (where all C bases are 5hmC) was glucosylated. Samples were then subjected to either two rounds of TET treatment or no TET treatment. DNA was ligated to the appropriate adapter and subjected to one of four conditions: no deamination, BS, pyridine borane or A3A. The pyridine borane workflow is equivalent to TAPS-β. The bases deaminated by each method (detected as T by sequencing) are noted, with structures of the deamination products at right, including the non-aromatic DHU. b) Percent reads C as determined by the methylated lambda phage spike-in. The sample with TET and bisulfite indicates efficient conversion of 5mC to 5fC/5caC by TET. c) Proportion of reads mapping to each spike-in are shown. Only borane deamination shows decreased reads mapping to the methylated lambda phage, with depletion dependent upon TET oxidation. d) qPCR detection of amplifiable DNA library after each deamination method. Shown are the p-values from paired two-tailed t-test (n = 4 for each deamination condition, 3e-4 between BS and borane, 2e-5 between BS and A3A). Data are presented as mean values +/− SD. e) Mean library size ± standard deviation for each deamination method. A representative BioAnalyzer trace is shown for each deamination method.