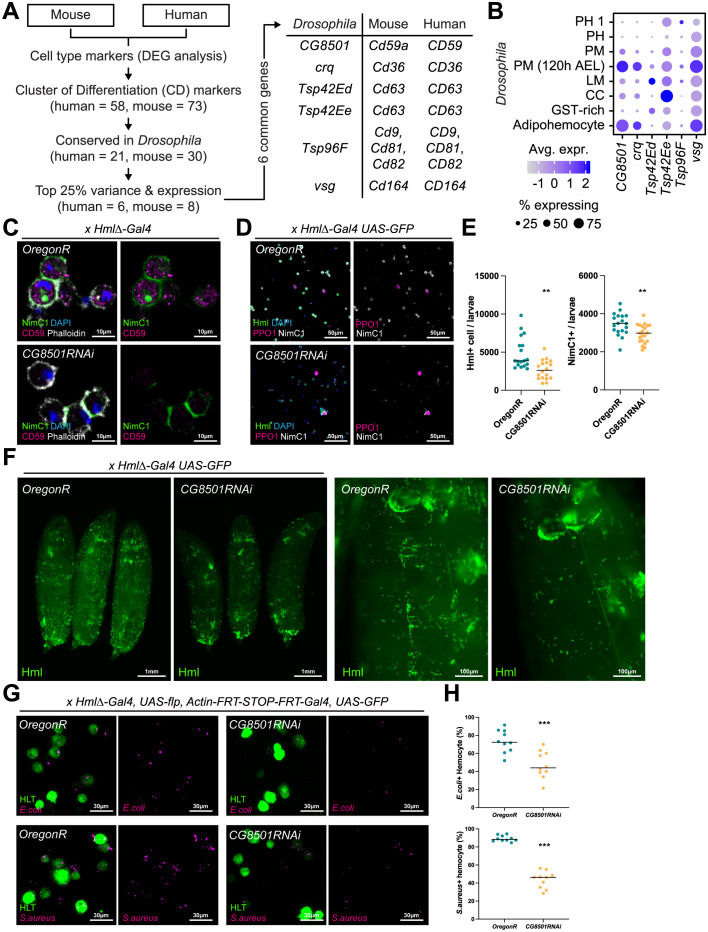
Fig 4. Drosophila CG8501, an orthologous gene of human CD59.
(A) Schematic illustration of the orthologous gene selection process. (B) Expression of CD orthologs in Drosophila hemocyte sub-populations. The dot color indicates the average level of expression, and the dot size represents the percentage of cells expressing the gene in each cell type. (C) Expression of protein CG8501 in the hemocyte detected by antibody staining against human CD59 protein. Protein CG8501 (magenta) was expressed in the cytosol and did not overlap with NimC1 (green) or phalloidin (white). Nuclei were stained by DAPI (blue). (D) Decrease in Hml+ hemocyte numbers in CG8501 RNAi expressing mutants. Compared to wild-type hemocytes (HmlΔ-Gal4 UAS-GFP Oregon R), knockdown CG8501 hemocytes (HmlΔ-Gal4 UAS-GFP CG8501 RNAi) show low Hml (green) and NimC1 (white) expressions. However, PPO1 (magenta)-positive mature crystal cells or the number of total hemocytes (DAPI, blue) did not change. (E) Quantification of Hml+ or NimC1+ hemocyte numbers in wild-type hemocytes (Oregon R) and knockdown CG8501 hemocytes (CG8501RNAi) (**p < 0.001). Horizontal bars indicate median values. (F) Whole mount images of wild-type larvae (Oregon R) and larvae with Hml+ blood cell (HmlΔ-Gal4 UAS-GFP CG8501 RNAi). Magnified images are on the right. (G) A visualization of the phagocytic ability of Drosophila hemocytes. Hemocytes (green) showed reduced phagocytotic ability against E. coli (magenta, top) and S. aureus (magenta, bottom) in CG8501 RNAi-expressing mutants (HLT-Gal4 UAS-GFP CG8501 RNAi). (H) Quantifications of the phagocytotic abilities of hemocytes against bacteria in panel G (***p < 0.0001). Horizontal bars indicate median values.