Fig. 2. NOS1AP is expressed by podocytes of mammalian glomeruli and localizes to actin-rich filopodia and podosomes.
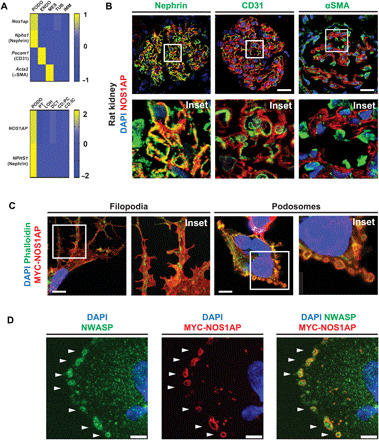
(A) NOS1AP mRNA (z-score) was predominantly expressed by podocytes from single-cell mRNA sequencing data (6, 40). Top: Nos1ap expression was highest in the podocyte cluster (Nphs1 and nephrin) relative to the endothelial cell cluster (Pecam1 and CD31), mesangial cell cluster (Acta2 and α-smooth muscle actin), and renal tubular and immune cells in murine glomeruli (6). Bottom: NOS1AP expression is similarly highest in the podocyte cluster relative to other nephron epithelial cell clusters from adult human kidney (40). PODO, podocytes; ENDO, endothelial cells; MES, mesangial cells; TUB, tubular epithelial cells; IMM, immune cells; PT, proximal tubular epithelial cells; LOH, Loop of Henle epithelial cells; DCT, distal convoluted tubular epithelial cells; CD:PC, collecting duct principal cells; CD:IC, collecting duct intercalated cells. (B) IF confocal microscopy imaging of rat kidney sections demonstrates NOS1AP colocalization (yellow) with podocyte slit diaphragm marker nephrin but not endothelial cell marker CD31 or mesangial cell marker αSMA. Insets are shown below each image. Scale bars, 25 μm. (C) In a human podocyte cell line, overexpression of MYC-tagged WT NOS1AP (MYC-NOS1AP) induced the formation of filopodia (left column) and peripheral ring structures (right column) in which NOS1AP colocalized with F-actin. (Images 26 hours after transfection.) Scale bars, 7.5 μm. (D) MYC-NOS1AP overexpression in a human podocyte cell line identifies peripheral ring structures as podosomes by colocalization of NOS1AP with NWASP (white arrows). Scale bars, 5 μm.
