Fig. 1. MYB proteins.
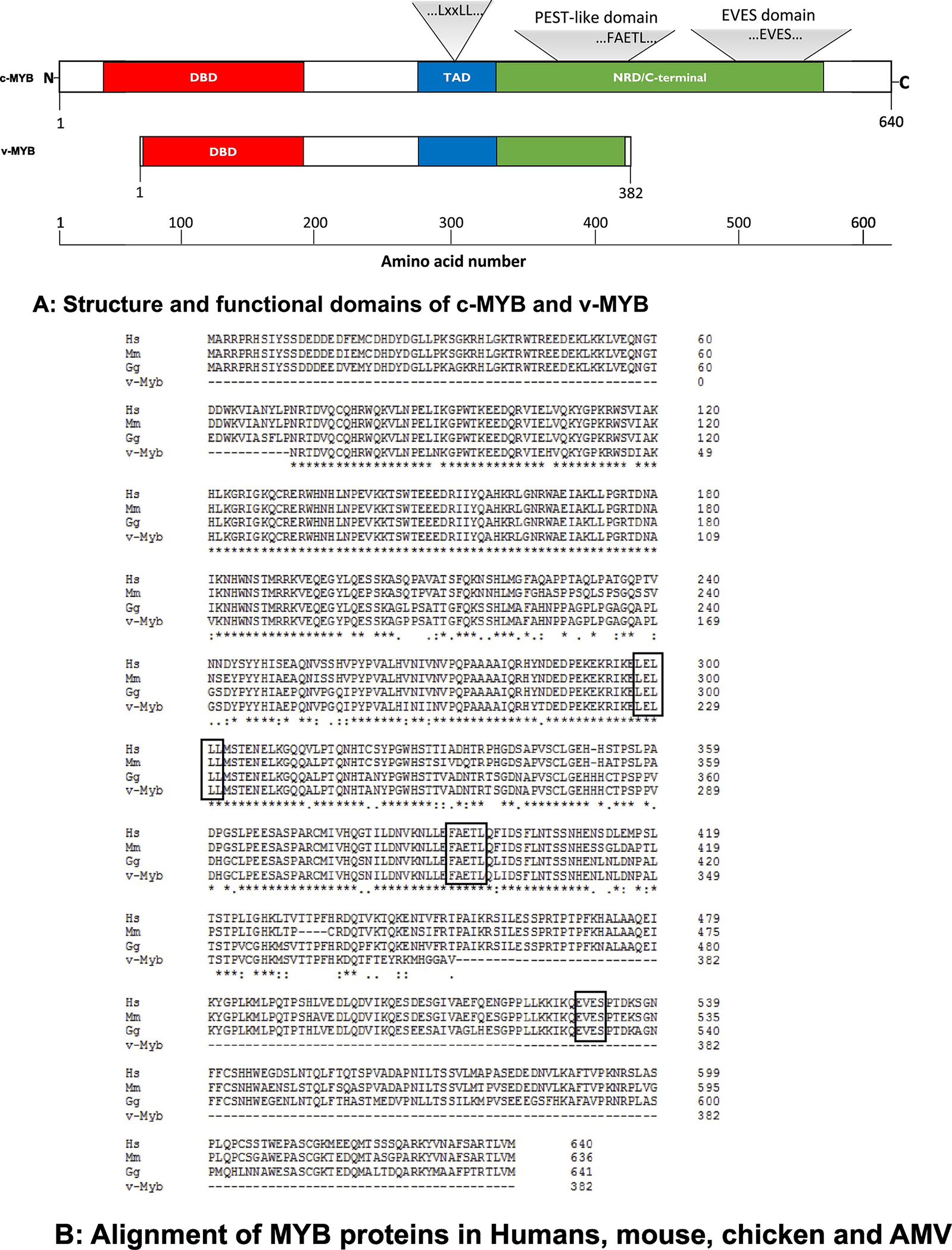
A: Structure and functional domains of c-MYB and v-MYB.
The schematic structure of c-MYB and its functional domains were drawn according to NCBI webpage, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/NP_005366.2? report=graph. DBD: DNA binding domain; TAD: transcription activation domain; NRD: negative regulatory domain. The locations for LxxLL, FAETL and EVES motives are depicted. v-MYB lacks NRD in the C-terminus, and hence, it is not surprising that it functions as a transcriptional activator all the time, a property that likely contributes to its role in leukemogenesis.
B: Alignment of MYB proteins in human, mouse, chicken and AMV.
The MYB proteins were aligned from Human (Hs for Homo sapiens, NP_005366.2), mouse (Ms for Mus musculus, NP_034978.3), chicken (Gg for Gallus gallus, P01103.1) and AMV (AAB31930.2). The identical residuals were marked as *, similar residuals were labeled as . or: The alignment was performed with software Clustal2.1. Motif sequences, “LxxLL”, “FAETL” and “EVES” are boxed.
