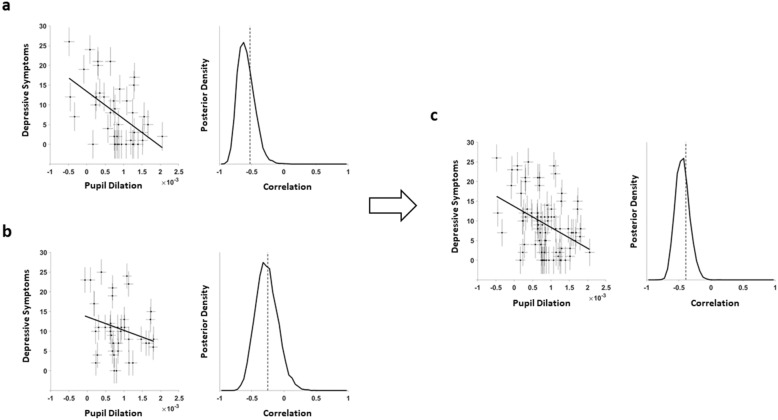
Figure 1.
Correlation pupil dilation and number of symptoms for depressed patients. (a) original study; (b) replication study; and (c) combined samples. Estimation of the correlation between pupil dilation during reward anticipation and the number of depressive symptoms taking measurement uncertainty of each measurement into account (represented by vertical and horizontal error bars) including regression lines (a, b, and c, left panels). The Bayesian model estimated the true correlation while accounting for measurement uncertainty by sampling from a multivariate Gaussian distribution, leading to a posterior distribution that indicates the likelihood of the modelled correlation (a, b, and c, right panels).