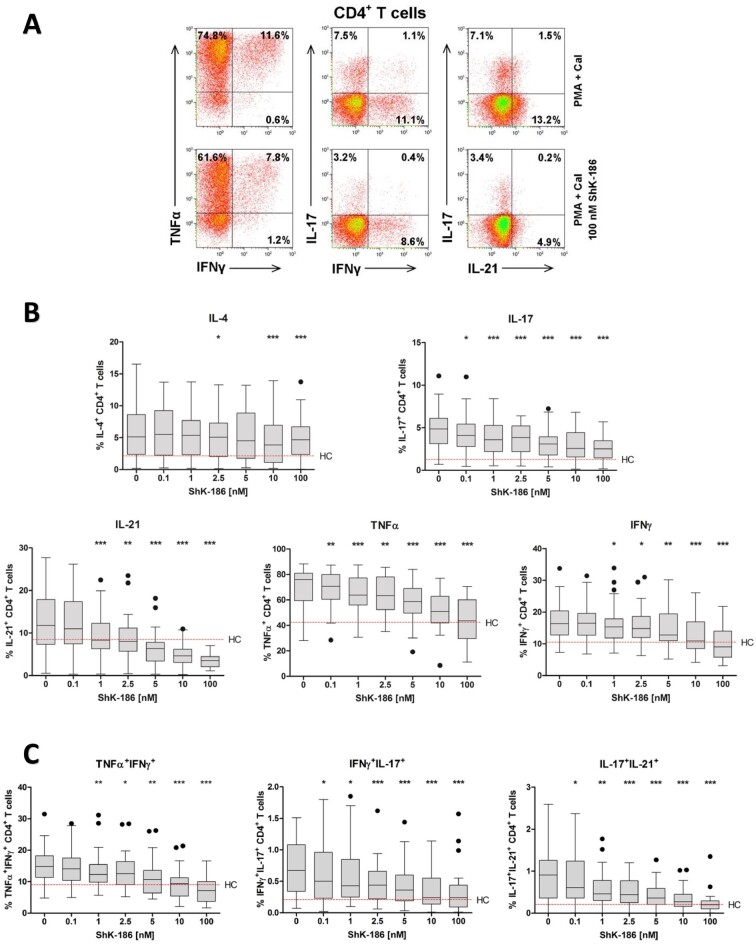
Figure 3.
Dose-dependent suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines by ShK-186 in CD4+TH cells from patients with GPA. Peripheral blood from patients with GPA and HCs was stimulated with PMA and CaI with and without increasing concentrations of ShK-186. Intracellular IL-4, IL-17, IL-21, TNFα and IFNγ cytokine production in CD4+TH cells was analysed using flow cytometry. (A) Representative flow cytometry dot plots of cytokine expression within CD4+ TH cells after stimulation in the presence (lower panels) and absence (upper panels) of ShK-186 from a patient with GPA in remission. (B) Percentages of cytokine-producing CD4+ TH cells after stimulation in the presence and absence of ShK-186 from patients with GPA in remission (grey box and whiskers; n = 27). (C) Percentages of TNFα+IFNγ+, IFNγ+IL-17+ and IL-17+IL-21+ within CD4+TH cells after stimulation in the presence and absence of ShK-186 from patients with GPA in remission (grey box and whiskers; n = 27). Box-and-whiskers plots (tukey): boxes represent median values and interquartile range. Red horizontal dashed line represents median percentage of cytokine production by CD4+TH cells from HCs. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs stimulated CD4+TH cells without ShK-186. CD4+TH: CD4+ T helper; CaI: calcium ionophore; GPA: granulomatosis with polyangiitis; HC: healthy control; phorbol myristate acetate