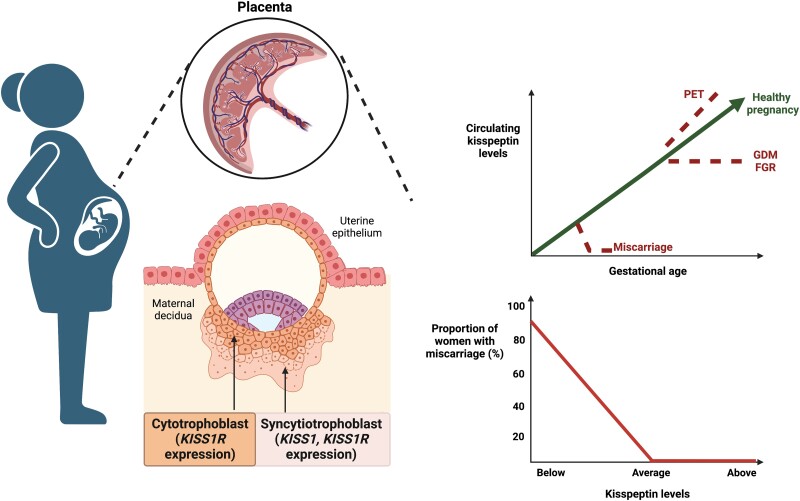
Figure 6.
The utility of KP in the prediction of pregnancy complications. KP regulates trophoblast invasion and placentation during pregnancy and has emerged as a promising biomarker to predict several adverse pregnancy complications. The KISS1 gene is abundantly expressed in syncytiotrophoblasts, whereas its receptor (KISS1R) is expressed in both cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts. Circulating KP levels increase linearly in healthy pregnancy but are reduced in miscarriage during early pregnancy. KP can accurately predict the risk of miscarriage with average/above average levels of KP being associated with a less than 1% risk of miscarriage. KP levels are reduced in FGR and GDM and raised in PET during the later stages of pregnancy. FGR, fetal growth restriction; GDM, gestational diabetes mellitus; KISS1, kisspeptin gene; KISS1R, kisspeptin receptor; KP, kisspeptin; PET, preeclampsia. Figure created with BioRender.com.