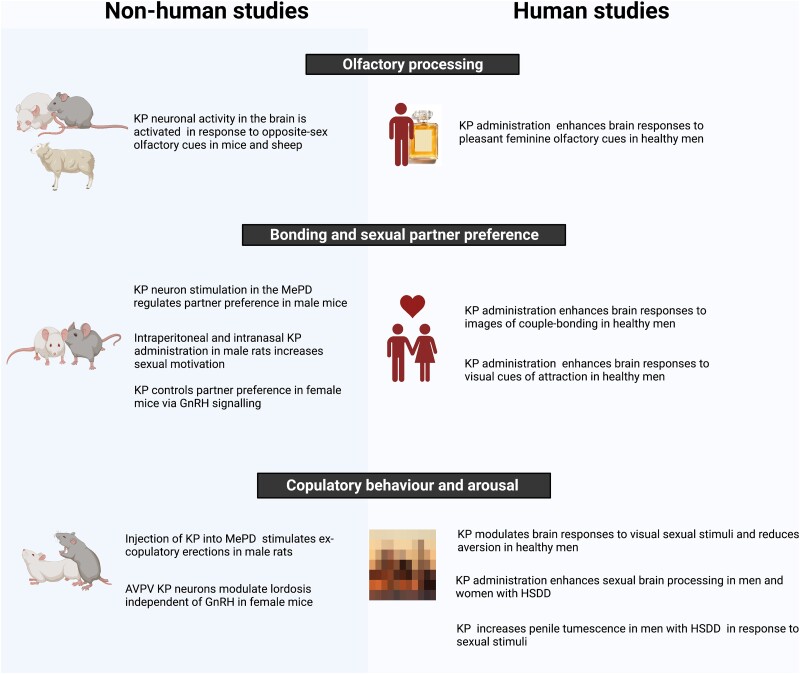
Figure 8.
The effects of KP signaling on key reproductive behaviors in rodents, sheep, and humans, including olfactory processing, sexual partner preference, copulatory behavior, and arousal and bonding. KP is widely expressed in limbic and paralimbic regions of the brain, which are involved in reproductive behaviors. Olfaction: KP expression and activity increased in several brain regions in response to opposite sex olfactory cues in male mice and female mice and ewes. In humans, KP administration enhanced limbic brain activity when men were exposed to a pleasant feminine scent. Sexual partner preference and bonding: Studies showed that the KP MePD neurons regulate partner preference in male mice, whereas intraperitoneal and intranasal administration of KP to male rats increases sexual motivation. When peripheral KP was administered to Kiss KO female mice, normal male-directed sexual preference was restored. In healthy heterosexual men, peripheral KP administration increased brain activity in aesthetic brain regions in response to viewing female faces. Copulatory behavior and arousal: KP stimulation in the MePD resulted in erections in male rats, whereas both peripheral and central KP administration to female mice robustly stimulated lordosis. In healthy heterosexual men, peripheral KP administration enhanced limbic brain activity when exposed to visual sexual stimuli. KP administration to males with HSDD deactivated brain regions involved in self- monitoring and introspection, and increased brain activity in sexual arousal centers, in response to watching erotic videos in the fMRI scanner. KP administration also led to increases in penile tumescence. KP administration to pre-menopausal women with HSDD, deactivated brain regions involved in inhibitory control and activated areas known to be activated in the context of sexual arousal in response to erotic visual cues. AVPV; anteroventral periventricular nucleus; fMRI, functional magnetic resonance imaging; GnRH, gonadotropin-releasing hormone; HSDD, hypoactive sexual desire disorder; KO, knockout; KP, kisspeptin; MePD, posterodorsal subnucleus of medial amygdala. Figure created with BioRender.com.