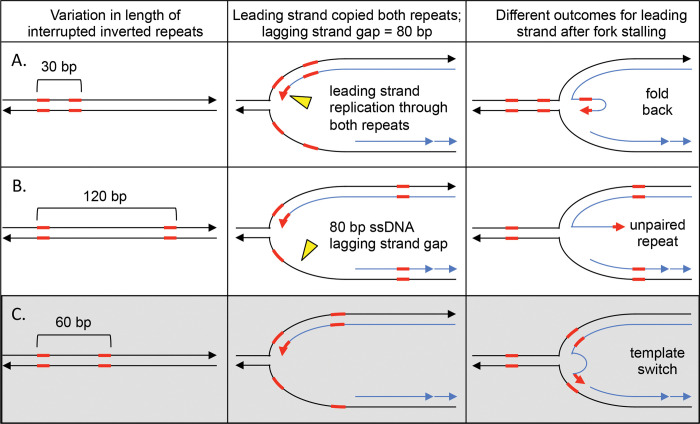
Fig 7. The size of single stranded gaps on the lagging strand at replication forks limits which interrupted inverted repeats contribute to inversion junctions.
Interrupted inverted repeats with a spacing of 40–80 kb are overrepresented in the inverted junctions of SUL1 amplicons. We propose that the size of the single stranded gap on the lagging strand is a primary contributor to this size selection. We illustrate this connection between interrupted inverted repeat size and lagging strand gap size for repeat spacing at three intervals. (A) If the repeats are in close proximity to one another (30 bp), during fork regression, the parental copies reform double stranded DNA and the displaced leading strand, containing the inverted repeats in single stranded form, are likely to self-hybridize. (B) If the repeats are at a distance that exceeds the average Okazaki gap on the lagging strand (120 bp), then fork regression leads to re-pairing of the parental strands of the left inverted repeat, while the right repeat had already been covered by an Okazaki fragment. This situation results in the repeat at the free 3’end with no template to which it can hybridize. (C) When both copies of the inverted repeats are within the size of an Okazaki gap (60 bp) then the left repeat will reform double stranded DNA between parental strands during fork regression. However, the left most copy on the leading strand still find its template in single stranded form on the lagging strand.