Figure 7.
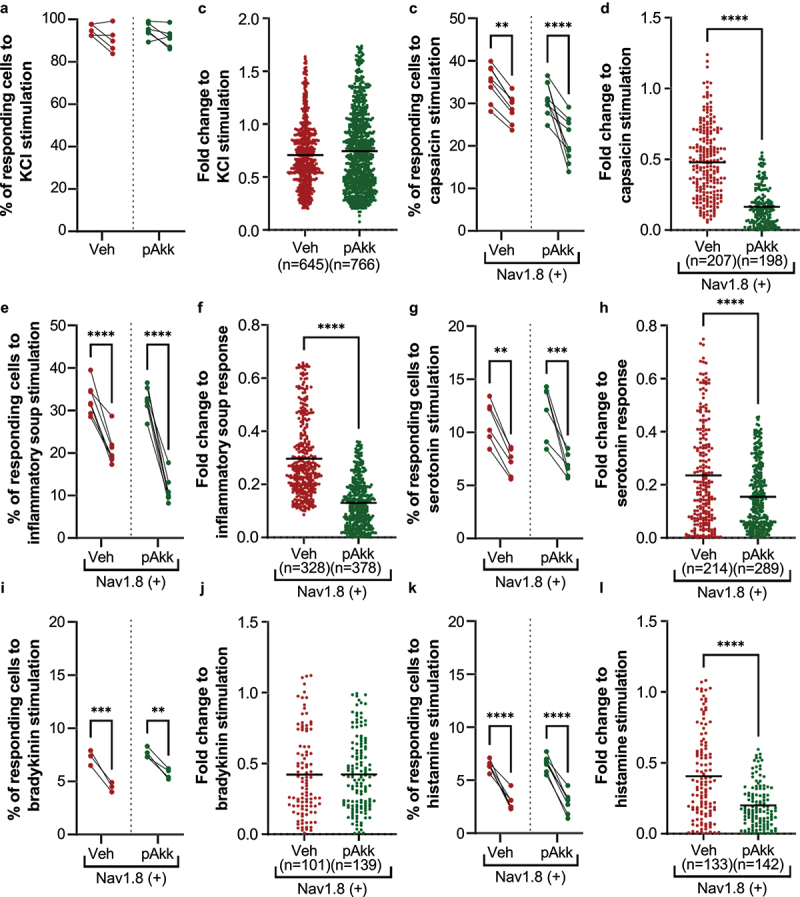
Neuromodulatory potential of pasteurized A. muciniphila on nociceptors from dorsal root ganglia innervating the colon. (a-b) neurons from all murine DRGs were activated with a pan-neuronal stimulation with KCl 30 mM. The percentage of neurons responding to the two KCl 30 mM simulations (a) and their activation level after the second KCl 30 mM stimulation (b) has been evaluated. (c-l) nociceptors (Nav1.8-cre-TdTomato positive neurons) from murine DRG innervating the colon were activated with several algogenic substances such as (c-d) capsaicin, (e-f) inflammatory soup, (G-H) serotonin 15 µM, (i-j) bradykinin 5 µM, or (k-l) histamine 15 µM. A ratiometric calcium imaging was used to visualize in real-time the neuronal activation level before and after incubation of pasteurized A. muciniphila (pAkk) or its vehicle. For the data analysis, the kinetic stimulation was studied for each viable neuronal cell. The percentage of neurons responding to each algogenic substances and the fold change in response intensity to the second stimulation (after vehicle or pasteurized A. muciniphila incubation) relative to the response intensity to the first stimulation of all viable neuronal cells belonging were calculated. Data are from two or three independent experiments. ****p < 0.0001.
