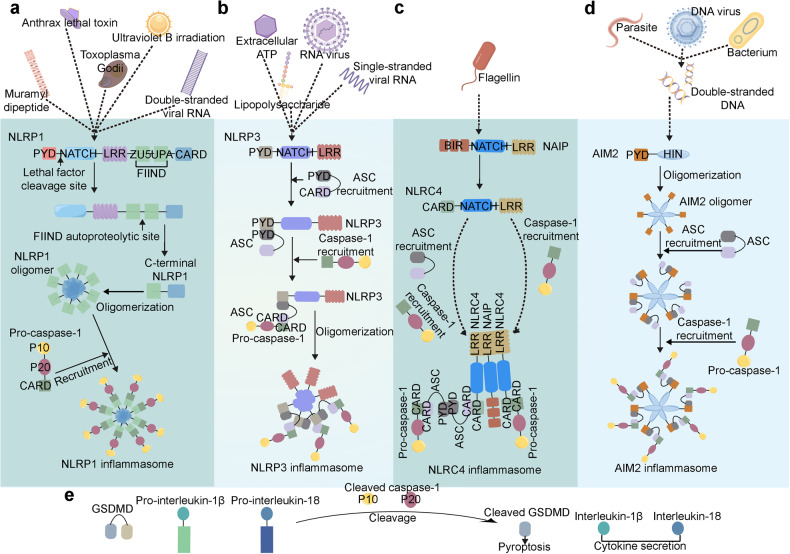
Fig. 3.
Representative pathways of the inflammasome activation. a Muramyl dipeptide, anthrax lethal toxin, Toxoplasma Godii, ultraviolet B irradiation, and double-stranded viral RNA can induce the cleavage of NLRP1, NLRP1 oligomerizes and leads to caspase-1 recruitment to form NLRP1 inflammasome. b Lipopolysaccharide, extracellular ATP, RNA virus, single-stranded viral RNA can activate the NLRP3, induce the ASC recruitment and following caspase-1 recruitment, and consequently form the NLRP3 inflammasome. c NAIP recognizes flagellin and interacts with NLRC4 to induce the ASC and caspase-1 recruitment and subsequent NLRC4 inflammasome formation. d Double-stranded DNA of parasite, bacterium, and DNA virus can be sensed by AIM2, then AIM2 oligomerized via its HIN domain, oligomerized AIM2 recruits ASC and caspase-1 respectively, and forms AIM2 inflammasome subsequently. e Inflammasomes cleave pro-caspase-1 to produce mature caspase-1 (also known as cleaved caspase-1 P10 and P20), cleaved caspase-1 cleaves GSDMD, pro-interleukin-1β, and pro-interleukin-18, cleaved GSDMD forms pyroptotic pore to execute pyroptosis, and interleukin-1β as well as interleukin-18 are released to extracellular space to regulate inflammation. The figure was created with the assistance of FIGDRAW