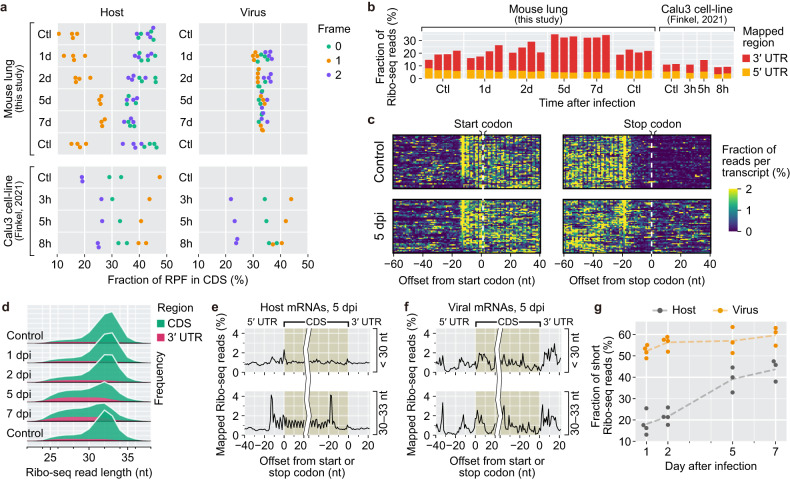
Fig. 2. Pseudoribosomal RNP interactions manifest in the lungs during SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis.
a Frame distributions of the 5′ ends of Ribo-seq reads within codons of all nonmitochondrial mRNAs. a, b, g, one replicate in the 5 dpi group and the other replicate in the 7 dpi group were excluded due to significant library quality issues. For a more detailed explanation, please refer to the supplementary methods. b The percentage of Ribo-seq reads aligned to the 3′ UTR and 5′ UTR in each sample. c Density maps of the Ribo-seq reads across the start codons and the stop codons of abundant mRNA transcripts. The alignment coordinates were determined on the basis of the 5′ ends of individual Ribo-seq reads. The number of each coordinate was normalized by the total count per gene. d Length distributions of the Ribo-seq reads that were uniquely aligned to CDSs and 3′ UTRs. e, f Metagene analysis of the long (30–33 nt) and short (<30 nt) Ribo-seq reads around start codons and stop codons of host nuclear mRNAs (e) and SARS-CoV-2 transcripts (f). g Relative fractions of the short Ribo-seq reads uniquely mapped to CDSs of host nuclear mRNAs and SARS-CoV-2 transcripts.