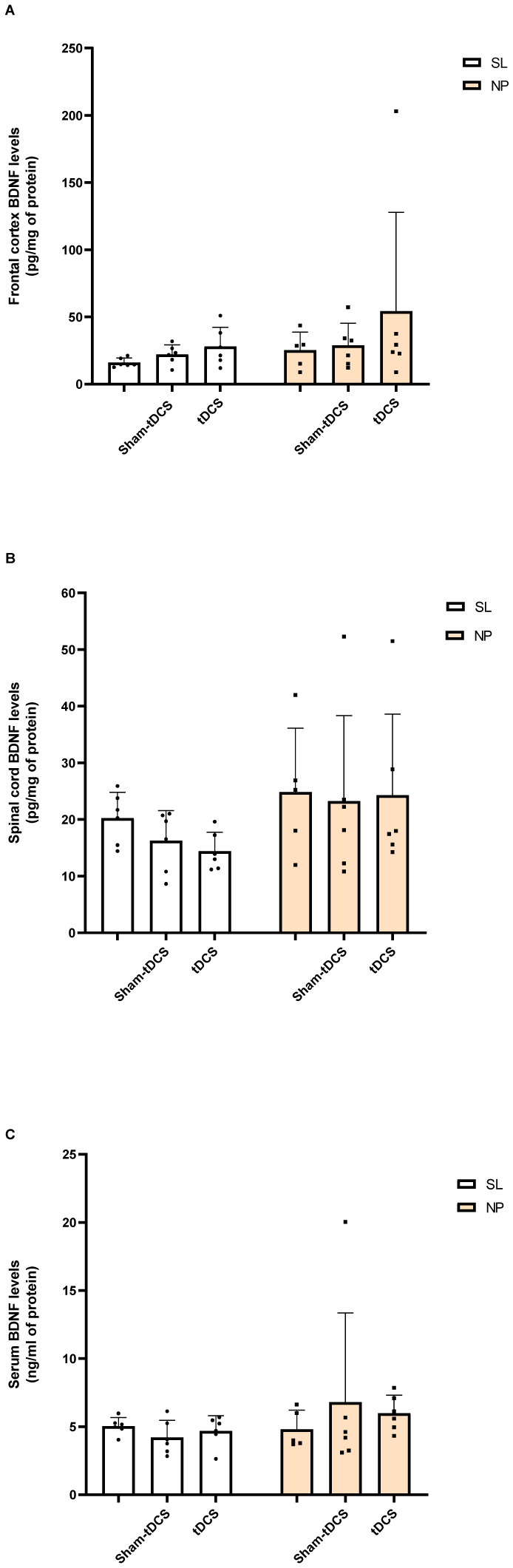
Figure 4. BDNF levels of rats in development at the long-term effect. Sham Lesion (SL); Sham lesion + sham-tDCS (SL + sham tDCS); Sham lesion + tDCS (SL + tDCS); Neuropathic pain (NP); Neuropathic pain + sham-tDCS (NP + sham-tDCS); Neuropathic pain + tDCS (NP + tDCS). Data are presented as the mean ± SD, (n = 5–6). Panel A: Frontal cortex BDNF levels: There were no effects of pain (F(1,29) = 1.635, P = 0.211) or tDCS F(2,29) = 1.272, P = 0.295) (Two-way ANOVA/Tukey, n = 5–6). Panel B: Spinal cord BDNF levels: There was an effect of pain (F(1,29) = 4.322 P = 0.0466). tDCS effect was not statistically significative different between groups (F(2,29) = 0.3370, P = 0.7167) and no interaction pain x tDCS was found (F(2,29) = 0.1971, P = 0.8222) (Two-way ANOVA/Tukey, n = 5–6). Panel C: Serum BDNF levels: there were no differences between groups for pain (F(1,29) = 1.530, P = 0.2260) or tDCS (F(2,29) = 0.1159, P = 0.8910) (Two-way ANOVA/Tukey, n = 5–6).