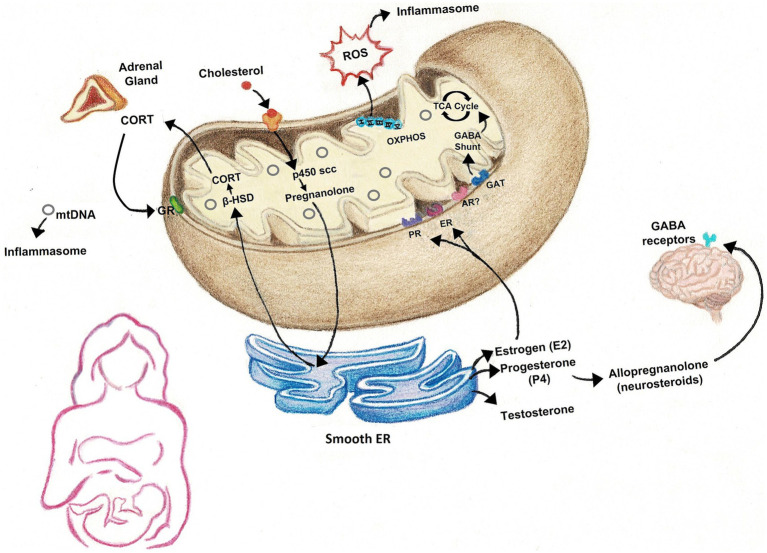
Figure 1.
Many of the physiological processes that occur in the peripartum rely on mitochondria. Mitochondria house the rate-limiting enzymes responsible for the synthesis of steroid hormones that fluctuate across the peripartum, including gonadal hormones, glucocorticoids, and neurosteroids, such as allopregnanolone. The electron transport chain and ATP synthase are responsible for the production of energy in the form of ATP, but also generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), which, along with cell-free mtDNA, can activate inflammasomes to promote inflammation. ROS may also have roles in cell signaling. GABA levels are also reported to fluctuate across the peripartum period and mitochondria are important sites of GABA catabolism. CORT, corticosterone/cortisol; ROS, reactive oxygen species; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; β-HSD, beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; p450 scc, cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; TCA cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; PR, progesterone receptor; ER, estrogen receptor; AR, androgen receptor; GAT, GABA transporter.