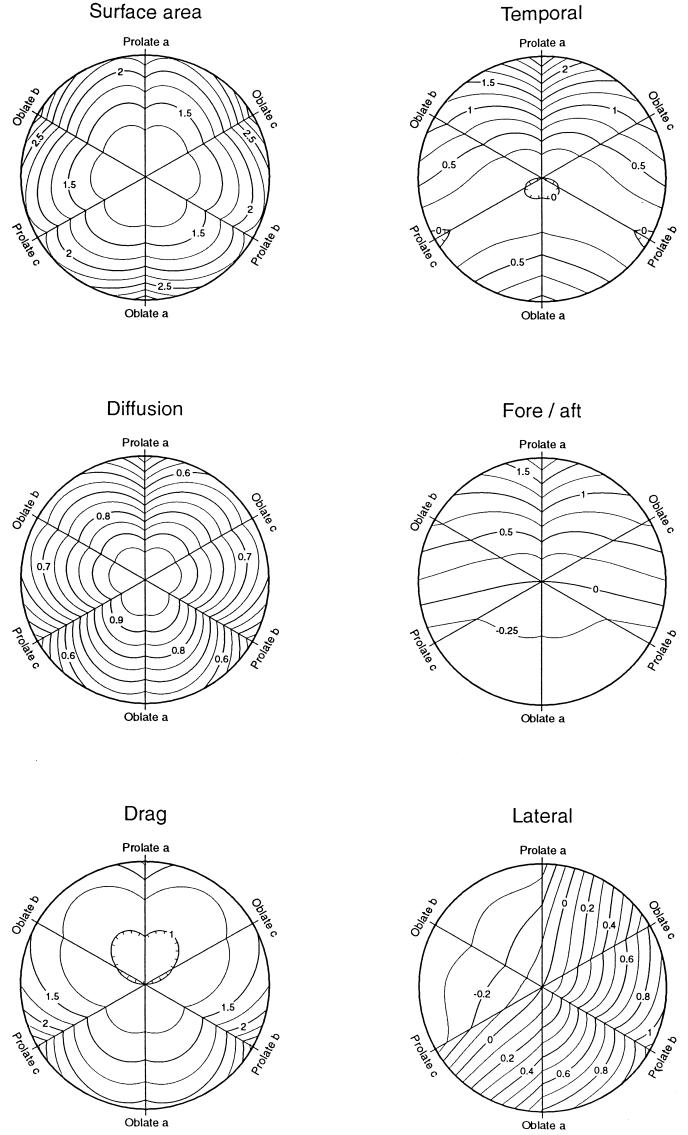
FIG. 2.
Contour plots of possible fitness components for equal-volume ellipsoids of all shapes. The values of the contours are relative to an equal-volume sphere. The sphere (a = b = c) is at the center, and the distance from the center is proportional to the negative log of the minimum radius of curvature occurring in each ellipsoid compared to the radius of the equal-volume sphere. At the outer edge of the plots, ellipsoids have a minimum radius of curvature of 1% that of the sphere. The three axes of the plots encompass the shapes in which two axes of the ellipsoid are identical (ellipsoids of revolution). At one end of each axis, prolate ellipsoids, with semiaxes equal to some permutation of (10, 10−1/2, 10−1/2), resemble rods, with axial ratios of 32; at the opposite end, oblate ellipsoids with semiaxes (10−4/5, 102/5, 102/5) resemble disks with axial ratios of 0.063. (Left) in Surface area, the contour values are the surface area of equal-volume ellipsoids; in Diffusion, the contours are the diffusion coefficients of equal-volume ellipsoids (equation 6); in Drag, the contour values are the frictional drag coefficient (fa′) for translation along axis a (equation 4). For the latter, the values within the innermost contour are less than 1, indicating that these shapes have a lower drag than an equal-volume sphere. (Right) Contour values are measures of the sensitivity a free-swimming organism can have in detecting the direction of a stimulus gradient by one of three mechanisms. In all three plots, the contour value is the log of a parameter proportional to the signal-to-noise ratio and sensitive to the shape of the organism. In Temporal, the parameter is (τa′3/2 fa′−1/2), which is proportional to the maximum signal-to-noise ratio for organisms employing temporal mechanisms and swimming in the direction of axis a. In Fore/aft, the parameter is (a τa′1/2), which is proportional to the maximum signal-to-noise ratio for organisms employing fore-and-aft comparisons. In Lateral, the parameter is (bτ′1/2), which is proportional to the signal-to-noise ratio for organisms employing lateral comparisons, and τ′ is the smaller of τa′ or τb′.