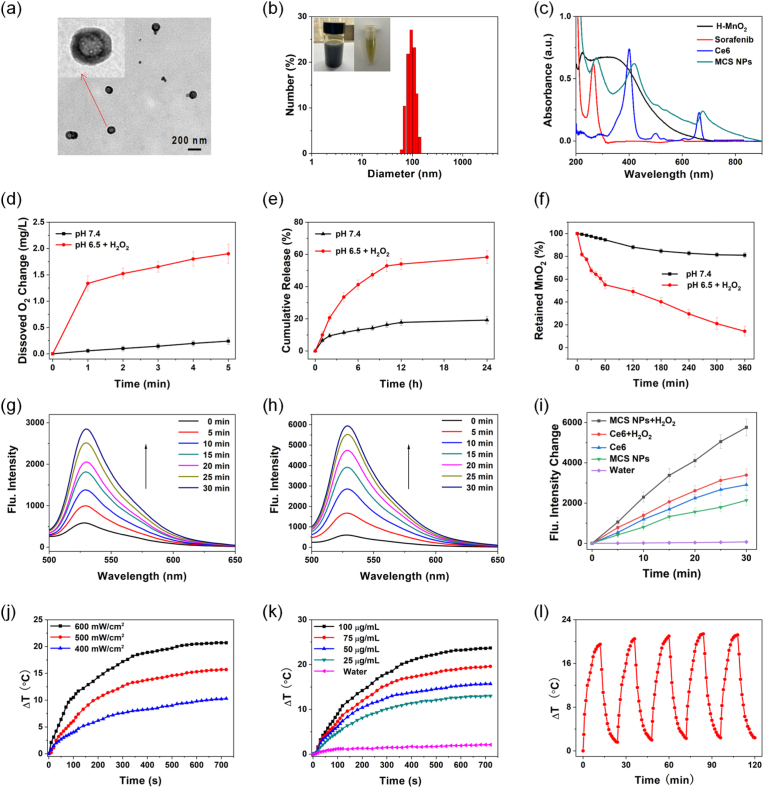
Fig. 2.
(a) TEM images of MCS NPs. The inset showed the magnified TEM images. (b) The DLS size distribution of MCS NPs in water. The inset showed the photos of MCS NPs. (c) Absorption spectra of H–MnO2, sorafenib, Ce6, and MCS NPs. (d) O2 production of MCS NPs dispersed with pH 7.4 in water and pH 6.5 in H2O2 solutions (100 μM), n = 3, mean ± SD. (e) The release rate of sorafenib from MCS NPs at pH 7.4 in water and pH 6.5 in H2O2 solutions (100 μM), n = 3, mean ± SD. (f) The degradation of H–MnO2 by measuring the absorbance spectra. n = 3, mean ± SD. (g, h) Fluorescence spectra (529 nm) of SOSG (10 μM) mixed with Ce6 without H2O2 and MCS NPs with H2O2 solutions, respectively. (i) Fluorescence intensity increases curves of SOSG from (g, h). (j, k) The temperature change of MCS NPs at different power and concentrations under 660 nm laser (500 mW/cm2), respectively. (l) Photothermal heating and cooling cycles of MCS NPs aqueous solution (75 μg/mL) with laser radiation (500 mW/cm2).