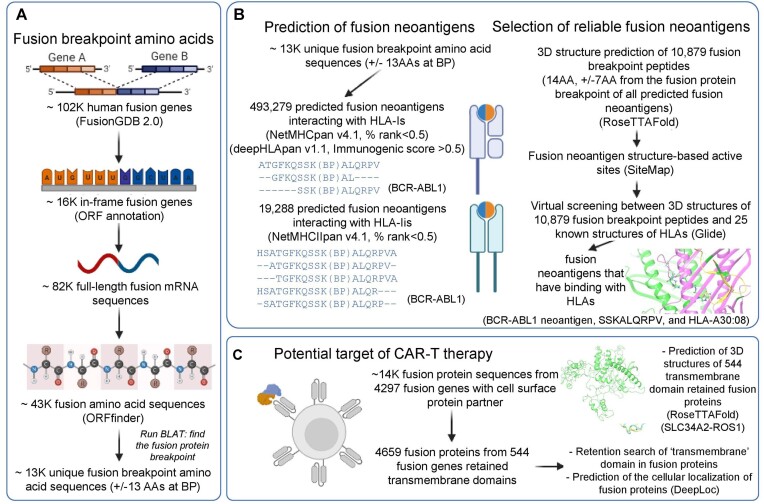
Figure 1.
Overview of FusionNeoAntigen. (A) Identification of fusion breakpoint amino acid sequences (±13 amino acids (AA) from the breakpoint). FusionNeoAntigen first annotates the open reading frames of ∼ 102K human fusion genes from FusionGDB2.0. For ∼ 16 in-frame fusion genes, we made ∼82K fusion full-length transcript sequences considering multiple breakpoints and gene isoforms. Using ORFfinder, we made ∼43K fusion amino acid sequences. By running the BLAT alignment tool, we identified the breakpoint position of the fusion protein sequences. From these fusion protein breakpoints, we made the ±13 AA fusion breakpoint peptide sequences. There were about 13K of unique fusion protein breakpoints that have these ±13 AA fusion breakpoint peptides. This is the material to predict the fusion-specific neoantigens. (B) Prediction of the fusion-specific neoantigens. We input ∼13K fusion breakpoint peptide sequences into NetMHCpan and deepHLApan. After filtering the tools’ criteria and checking the position of the neoantigens whether it is across the breakpoint, we identified ∼500K and 20K fusion-specific neoantigens in ∼10K and ∼ 7K unique fusion breakpoints with HLA-Is and HLA-IIs, respectively. To highlight the bindings between the fusion-specific neoantigens and HLAs, we performed the virtual screening between ∼10K predicted fusion neoantigens using RoseTTAFold and 25 HLA-Is that have known 3D structures from the PDB. (C) Identification of the potential target of CAR-T therapy. FusionNeoAntigen provides not only the fusion-specific neoantigens but also the potential target of CAR-T therapy in fusion proteins. First, we overlapped ∼14K in-frame fusion genes with 4297 cell surface genes. Then, there were 544 fusion proteins that had a cell surface protein as one of the fusion partner proteins and retained the transmembrane domains. For these, we predicted their potential 3D structures using RoseTTAFold and also predicted the cellular localization of the fusion proteins using DeepLoc.