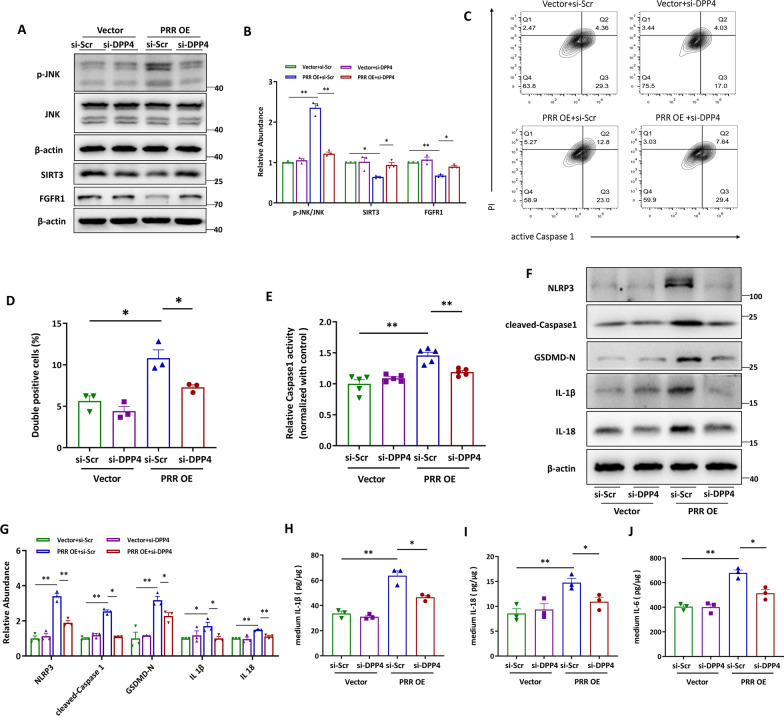
Fig. 6.
PRR exerted pyroptotic effects through DPP4-mediated signaling. A and B Representative western blot analyses (A) and quantitative data (B) showed that knocking down DPP4 by siRNA in HK-2 cells diminished PRR overexpression induced phosphorylation of JNK, and restored PRR overexpression reduced SIRT3 and FGFR1 expression (n = 3). C and D Flow cytometry analysis showed that knocking down DPP4 reduced PRR overexpression induced frequency of active Caspase1+PI+ HK-2 cells (C) and quantitative data (D) (n = 3). E PRR was silenced in HG stimulated HK-2 cells, and the Caspase1 activity in cell lysis was determined by kits. f and g Western blot analyses (F) and quantitative data (G) showed that DPP4 siRNA blocked HG-induced NLRP3, cleaved-Caspase1, GSDMD-N, IL-1β and IL-18 expression in HK-2 cells (n = 3). H and I DPP4 was knocked down in PRR overexpressed HK-2 cells, and the IL-1β (H), IL-18 (I) or IL-6 (J) concentration in the culture medium was determined by ELISA, and then normalized by protein concentration in cell lysates (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SEM of biologically independent samples. ∗ P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01. One-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data among multiple groups, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test