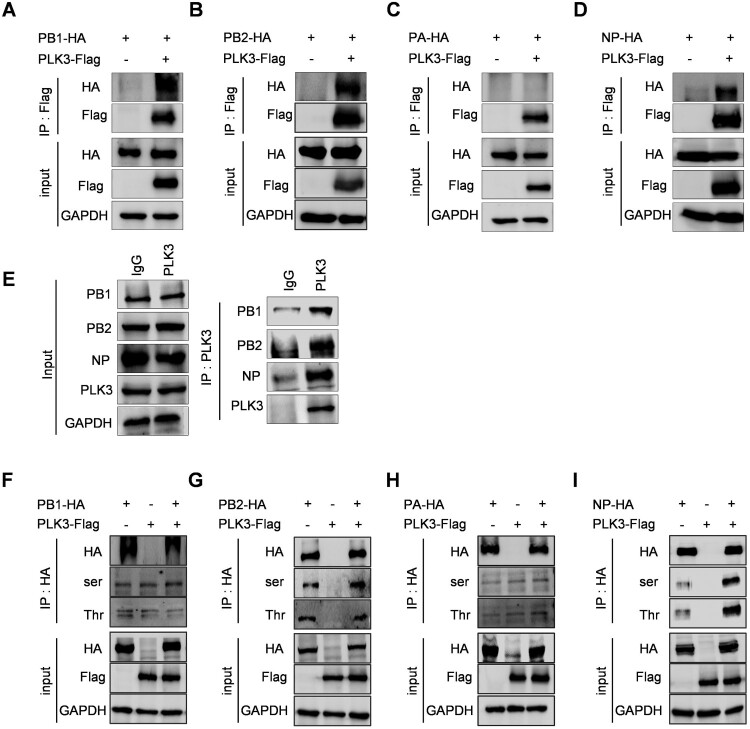
Figure 2.
PLK3 interacted with NP and promoted NP phosphorylation. (A, B, C, and D) Interactions between PLK3 and viral RNP components. The expression plasmid of PLK3-Flag was respectively cotransfected with PB1-HA (A), PB2-HA (B), PA-HA (C), or NP-HA (D) in HEK293T cells. The cell lysates were collected at 24 h post-transfection. Co-IP assays were performed using an anti-Flag antibody to precipitate viral RNP components which interacted with PLK3, followed by western blotting to detect PLK3 using an anti-Flag antibody and PB1, PB2, PA, and NP using an anti-HA antibody. GAPDH served as a loading control in all of these experiments. (E) Interactions between endogenous PLK3 and viral RNP components in the context of viral infections. NPTr cells were infected with SIV-H1N1/2009 at a MOI of 0.01. The cell lysates were collected at 24 h post-infection. Co-IP assays were performed using anti-IgG and anti-PLK3 antibodies to precipitate viral RNP components which interacted with PLK3, followed by western blotting to detect PLK3 using an anti-PLK3 antibody and PB1, PB2, PA, and NP using endogenous antibodies. GAPDH served as a loading control in all of these experiments. (F, G, H, and I) Effects of PLK3 on the phosphorylation of viral RNP components. The expression plasmid of PLK3-Flag was respectively cotransfected with PB1-HA (F), PB2-HA (G), PA-HA (H), or NP-HA (I) in HEK293T cells. The cell lysates were collected at 24 h posttransfection, then, PB1-HA, PB2-HA, PA-HA, and NP-HA were immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody, and the associated phosphorylated serine/threonine of PB1, PB2, PA, and NP were detected using anti-p-serine/threonine antibodies. GAPDH served as a loading control in all of these experiments.