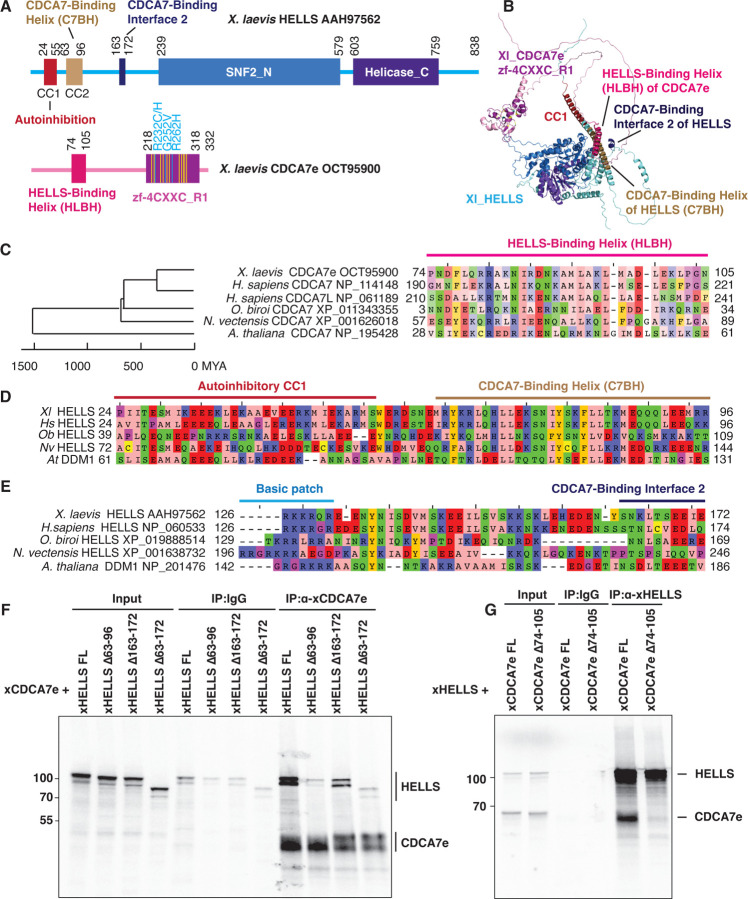
Fig. 4. Identification of HELLS-CDCA7 interaction interface.
(A) Schematics of X. laevis HELLS and CDCA7e. Positions of the signature 11 conserved cysteine residues and 3 ICF disease-associated mutations in CDCA7e are marked in yellow and cyan, respectively. CC1 is a coiled-coil domain important for autoinhibition. (B) The best predicted structure model of X. laevis HELLS-CDCA7e complex by AF2. (C) Sequence alignment of the putative HELLS/DDM1-binding interface of CDCA7. (D) Sequence alignment of the putative CDCA7-binding interface 1 in HELLS/DDM1. (E) Sequence alignment of the putative CDCA7-binding interface 2 in HELLS. (F) Immunoprecipitation by control IgG or anti-CDCA7e antibodies from Xenopus egg extracts containing 35S-labeled wild-type or deletion mutant of X. laevis HELLS and CDCA7e. (G) Immunoprecipitation by control IgG or anti-HELLS antibody from Xenopus egg extracts containing 35S-labeled HELLS and wild-type or Δ74–105 deletion mutant of CDCA7e. Autoradiography is shown in F and G.