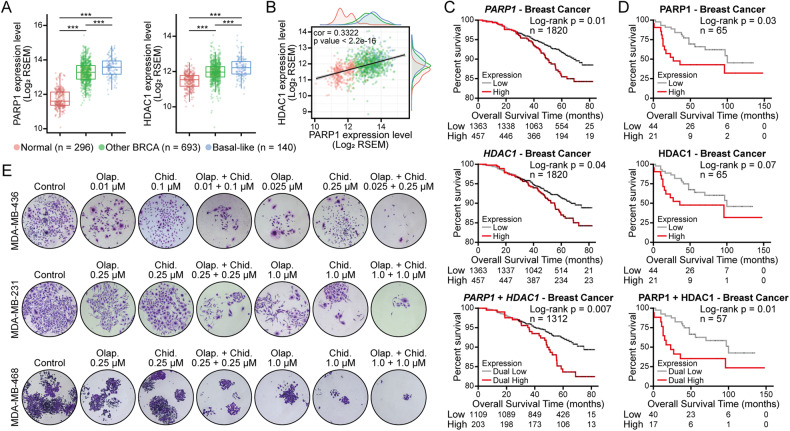
Fig. 1. Human breast tissue expression of PARP and HDAC and its correlation and synergistic anticancer efficacy in vitro.
A Transcript expression levels of PARP1 and HDAC1 in different breast samples from TCGA TARGET GTEx study (Normal: normal tissues; Other BRCA: other breast cancer tissues, non-basal-like subtype tissues; Basal-like: basal-like subtype tissues). ***p < 0.001. B Correlation of PARP1 and HDAC1 transcriptomic expression levels in human breast cancer tissues and normal tissues (normal tissues, n = 296; other BRCA tissues, n = 693; basal-like subtype tissues, n = 140). C, D Kaplan–Meier overall survival curves of human breast tumors according to PARP1 and HDAC1 gene C or protein D expression levels, with auto select best cut-off selected. Differences were assessed using the log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. E MDA-MB-436, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-468 cells were treated with different concentrations of PARP inhibitors (olaparib) and HDAC inhibitors (chidamide) alone or in combination for approximately 14 days, and cell growth was measured by colony formation assay. Olap., olaparib; Chid., chidamide.