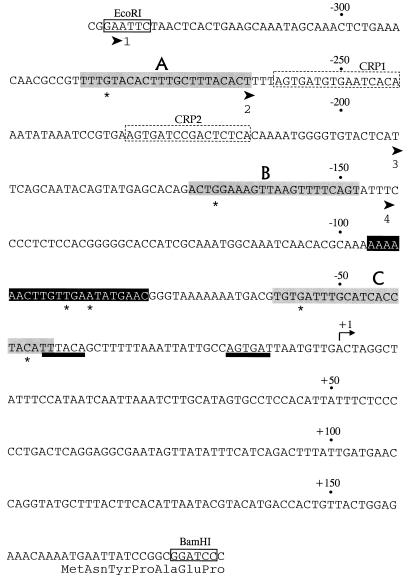
FIG. 1.
The tpl promoter and associated regulatory elements. Only the nucleotide sequence of the messenger-equivalent strand is shown. The coordinate system has been changed from the system in the original publication (3) by assigning +1 to the start point of transcription. DNA fragments used in the functional analysis of the tpl promoter were synthesized by PCR, with pRVT1 (3) as the template. Cleavage sites for restriction endonucleases EcoRI and BamHI were installed at the indicated locations (coordinates −329 and +180) in order to facilitate the construction of single-copy reporter systems. The EcoRI-BamHI fragment was cloned into pUC19, which contains a PstI site downstream of the BamHI site. The fragment from pUC19-tpl generated by EcoRI-PstI digestion was used for DNase I footprinting experiments. The 5′ end points of three truncated derivatives of the tpl promoter are shown as broad arrowheads labeled 2, 3, and 4 at coordinates −262, −193, and −144. The −10 and −35 recognition elements are underlined with heavy black lines. The target sites for cAMP-CRP (CRP1 and CRP2) are outlined with broken lines. TyrR boxes, named A, B, and C, are shaded. Residues marked by asterisks (−280, −166, −55 and −40) are the locations of TyrR operator mutations or IHF mutations (see text). The IHF binding site is presented in white letters on black.