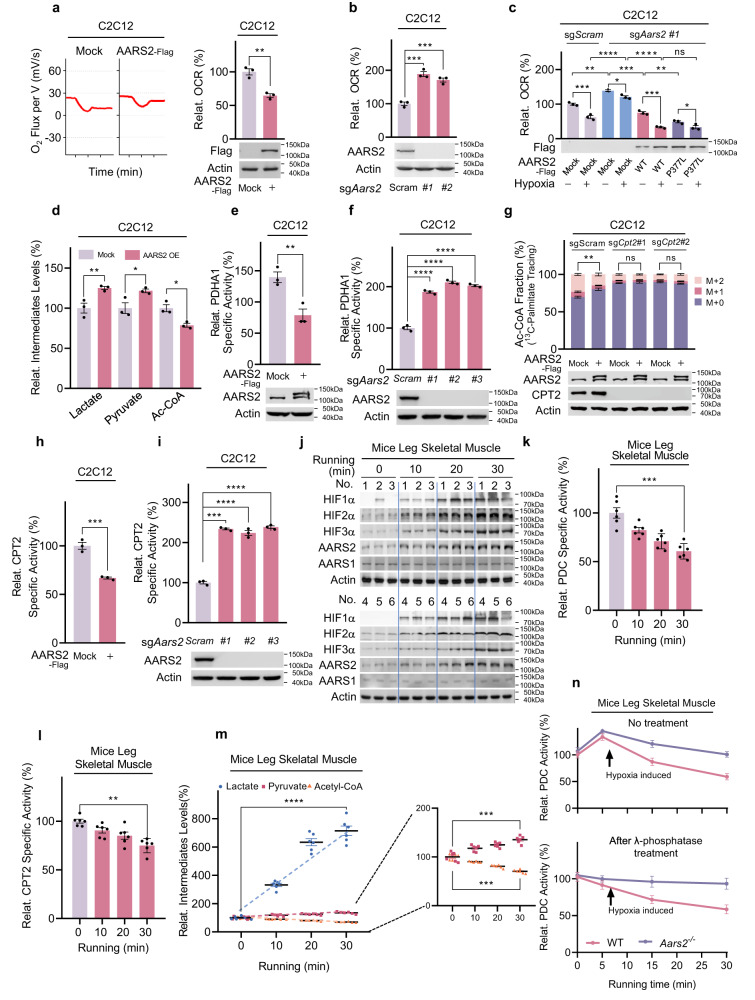
Fig. 3. AARS2 inhibits Ac-CoA production and OXOPHOS.
a, b AARS2 regulates OCR. The effects of overexpressing AARS2 (left, OROBOROS Oxygraph-2K measurements; right, quantitation) (a), and Aars2 KO using independent sgRNAs (b) on OCR (O2 influx per volume cells, mV/s) were determined (n = 3). c AARS2 regulates OCR in response to oxygen levels. The effects of re-introducing wide-type AARS2 or P377L into Aars2−/− C2C12 cells were determined in cells under normoxic conditions and cells which were exposed to hypoxia for 8 h (n = 3). d AARS2 regulates metabolite levels. Relative levels (to those of C2C12 cells) of lactate, pyruvate, and Ac-CoA in C2C12 cells and C2C12 cells overexpressing AARS2 (n = 3) were evaluated. e, f AARS2 regulates PDHA1-specific activity. Relative specific activities (to those from C2C12 cells) of PDHA1 purified from C2C12 cells overexpressing AARS2 (e) and Aars2 KO C2C12 cells (f) were determined (n = 3). g AARS2 regulates CPT2-mediated Ac-CoA production. The percentages of unlabeled (M + 0), single labeled (M + 1), and double-labeled (M + 2) Ac-CoA from 13C-palmitate in C2C12 cells and C2C12 cells in which Cpt2 had been knocked out using independent sgRNAs, were determined with or without AARS2 overexpression; 100 μM 13C-palmitate chasing was performed for 12 h (n = 3). The M + 2 percentages in C2C12 cells with and without AARS2 overexpression were compared for significance. h, i AARS2 regulates CPT2-specific activity. The relative specific activity (to those from C2C12 cells) of CPT2, isolated from both AARS2-overexpressing (h) and Aars2 KO C2C12 cells (i) was determined (n = 3). j Running induces HIFαs and AARS2 expression in mouse leg skeletal muscles. HIF1α, HIF2α, HIF3α, AARS1, and AARS2 levels in mouse leg skeletal muscles were determined before and after running for the indicated durations (n = 6). k, l Running inactivates PDC and CPT2 in vivo. The relative (to those of resting mice) specific activities of PDC (k) and CPT2 (l) in mouse leg skeletal muscles were determined after mice started running for indicated durations (n = 6). m Endurance running-induced lactate accumulation and Ac-CoA reduction. The lactate, pyruvate, and Ac-CoA levels in mouse leg skeletal muscles were determined after mice were allowed to run for the indicated durations (n = 6). n AARS2 inactivates PDC via a mechanism other than phosphorylation. The relative PDC activities (to protein amount) of wild-type and Aars2−/− mouse leg skeletal muscles sampled at different time points after starting to run with or without dephosphorylation induced by λ phosphatase, were determined (n = 6). The activities at time 0 were set as 100%. All data are reported as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was assessed by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test and two-way ANOVA: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; ns no significance.