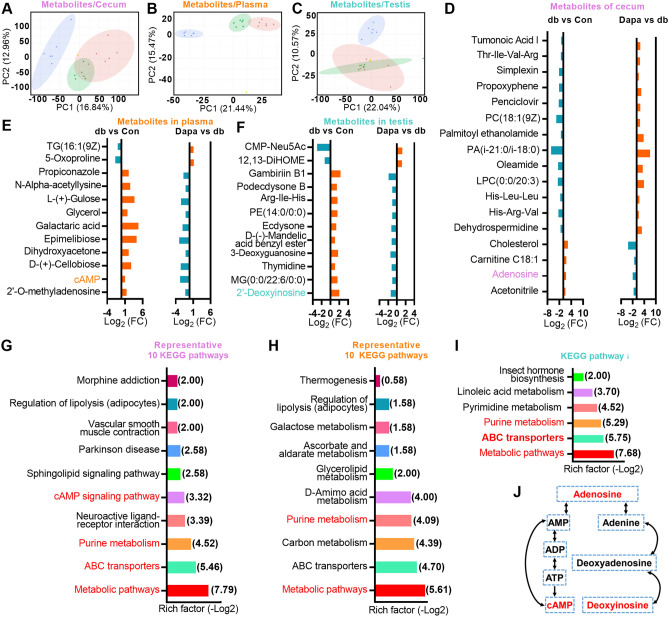
Figure 3.
Alterations in microbial, plasmatic, and testicular metabolic profiles caused by dapagliflozin administration. (A–C) Principal component analysis (PCA) plots of metabolomic profiles from cecum (A), plasma (B), and testis (C). (D–F) The Log2-fold change (Log2FC) of the 17, 12 and 12 metabolites that were rescued by dapagliflozin in cecum (D), plasma (E) and testis samples (F). (G–I) Representative 10, 10 and 6 KEGG pathways of the dapagliflozin rescued microbial (G), plasmatic (H) and testicular metabolites (I). Rich factor was shown as -Log2 and the enriched KEGG pathways involved adenosine, cAMP and deoxyinosine were presented in red. (J) The relationship of adenosine, cAMP and deoxyinosine in the purine metabolism pathway.