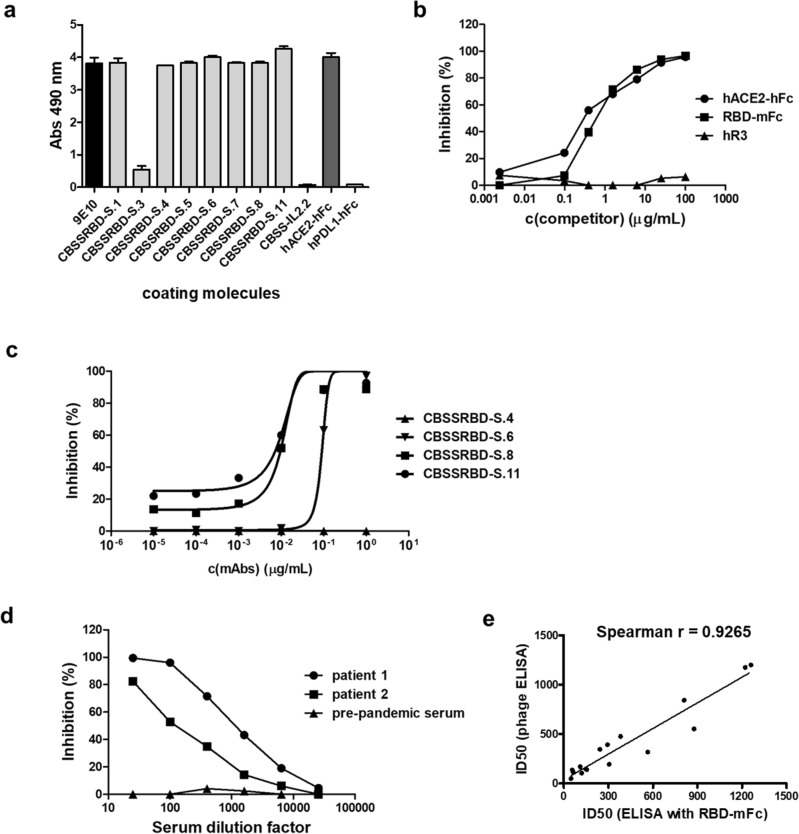
Figure 2.
Antigenicity and biological activity of phage-displayed Wuhan-Hu-1 RBD. Phages displaying RBD (1011 viral particles/mL) were incubated on polyvinyl chloride microplates coated with the anti-c-myc tag antibody 9E10, anti-RBD mAbs (CBSSRBD-S.1-CBSSRBD-S.11), and a recombinant protein comprising human ACE2 extracellular domain (ECD) fused to human IgG1 Fc (hACE2-hFc). Anti-IL2 CBSS-IL2.2 mAb and the fusion protein hPDL1-hFc were used as unrelated coating molecules to assess non-specific background levels. Bound phages were detected with an anti-M13 PVIII mAb conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (a). Binding of phage-displayed RBD to immobilized hACE2-hFc was inhibited by two soluble recombinant fusion proteins: hACE2-hFc itself and a second protein comprising RBD fused to mouse IgG2a (RBD-mFc) (b), and not by a humanized antibody targeting EGF Receptor (hR3) included as negative control. Inhibition by neutralizing anti-RBD antibodies CBSSRBD-S.6, CBSSRBD-S.8 and CBSSRBD-S.11 (c) and by sera of COVID-19 convalescent patients (d) was also shown. Non-neutralizing CBSSRBD-S.4 mAb and negative pre-pandemic serum were used as negative controls in each case. Sera from sixteen COVID-19 convalescent patients were evaluated by the above-described competition assay and in a similar experiment using RBD fused to mouse IgG2a Fc (RBD-mFc) as the probe and anti-mouse IgG conjugated to HRP for detection. Half-maximal inhibitory dilution (ID50) for every sample in each assay was determined after fitting the data to sigmoidal inhibition curves. Spearman correlation was used to determine the association between the ID50 values obtained in both formats (e). A significant correlation was observed (p < 0.0001).