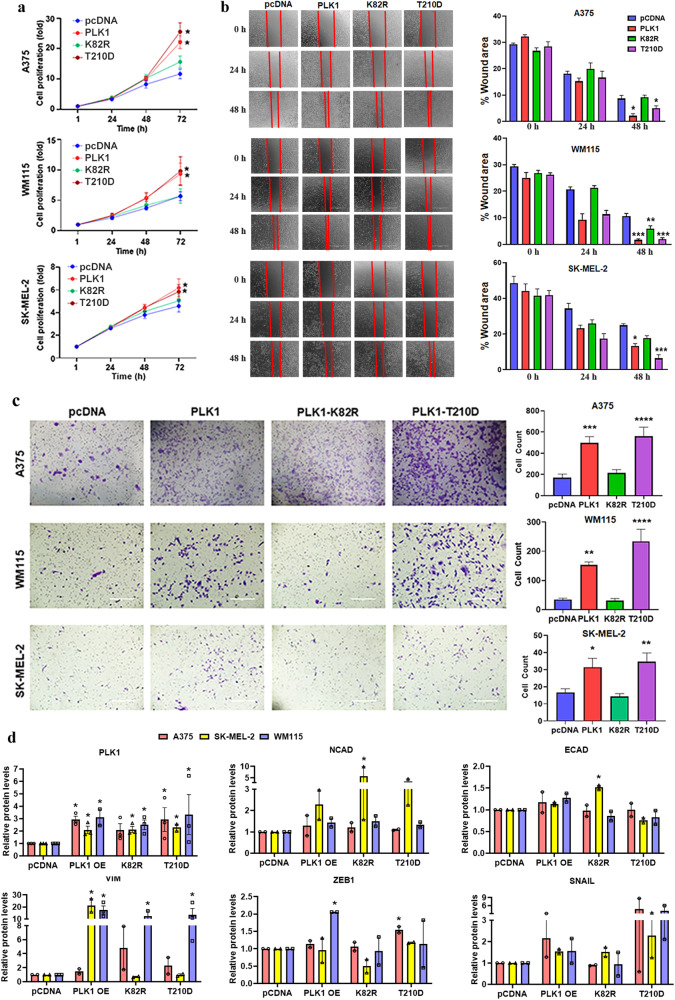
Fig. 3. Cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT-related proteins affected by PLK1 wild-type and mutant kinase overexpression activity in melanoma cells.
a Cell proliferation assay was performed using RealTime-Glo MT Cell Viability Assay (Promega) in PLK1-modulated melanoma cells (PLK1-wild type; K82R- constitutively inactive; T210D- constitutively active) till 72 h. b Cell migration was analyzed by wound healing assay in PLK1-modulated melanoma cells at 0, 24, and 48 h post-wound creation. c Cell invasion was analyzed by Matrigel invasion chambers using PLK1-modulated melanoma cells at 24 h. For a–c, the quantitative data are presented as mean ± SEM with statistical significance compared to empty vector (pcDNA) control (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001) in ≥2 biological replicates with ≥3 technical replicates (2-3 images per replicate for migration and invasion assay). Scale Bar=400 µm. d Simple Western immunoblot analysis showing expression of EMT-related proteins in PLK1-modulated melanoma cells. The relative protein levels normalized to total protein are presented as mean ± SEM with statistical significance compared to shNS control (*p < 0.05) in ≥2 biological replicates of each cell line. Statistical significance was determined using one- or two-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD tests.