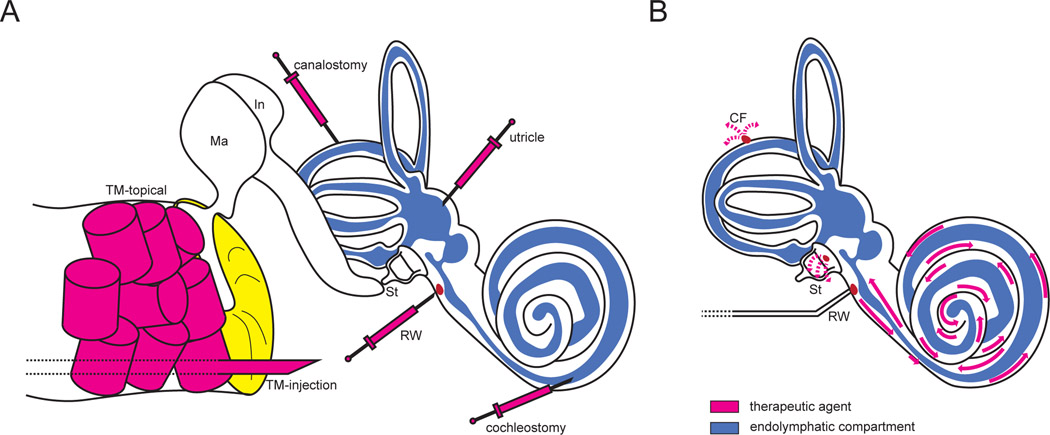
Figure 1.
Well-described delivery techniques for cochlear gene therapies. (A) A variety of delivery methods have been developed for delivery to the endolymphatic and perilymphatic compartments. Topical transtympanic delivery utilizes absorbable packing saturated in a gene therapy agent and is reliant on diffusion across the tympanic membrane and round window to achieve therapeutic levels of the drug within the cochlea (magenta cylinders). Transtympanic injection bypasses the tympanic membrane to inject within the middle ear space (large magenta needle). The remaining approaches (small magenta needles) offer direct delivery to the endolymphatic compartment, perilymphatic compartment (round window), or both (utricle, canalostomy, cochleostomy, utricle). B) Round window membrane injection combined with posterior or horizontal semicircular canal venting facilitates efficient, atraumatic vector transduction in murine models. In humans and non-human primates, a similar approach is proposed using a stapes footplate/oval window vent, which can be accessed via a transcanal tympanoplasty or mastoidectomy approach.
CF: canal fenestration; In: incus; Ma: malleus; RW: round window; St: stapes; TM: tympanic membrane.