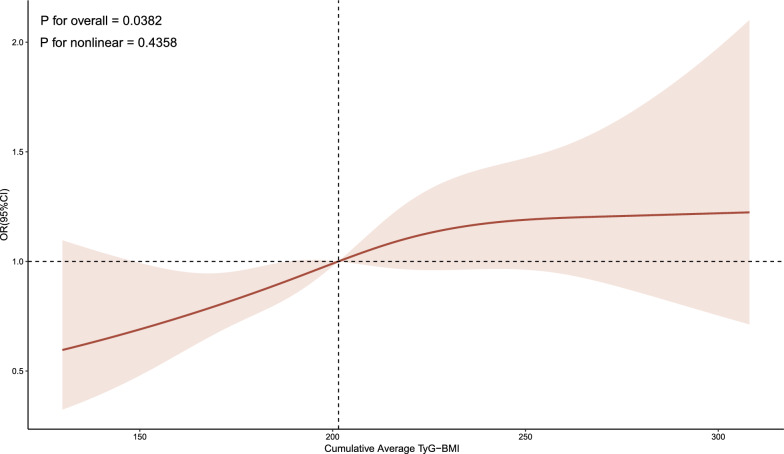
Fig. 3.
Association between the cumulative average TyG-BMI and incident CVD. The model was adjusted for age, gender, smoking status, drinking status, SBP, DBP, HbA1c, TC, HDL-c, LDL-c, residence (hukou), education level, marital status, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, liver disease, kidney disease, antihypertensive treatment, lipid-lowering treatment and hypoglycaemic treatment. SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin A1c; TC, total cholesterol; HDL‐c, high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-c, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TyG-BMI, triglyceride glucose-body mass index; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval