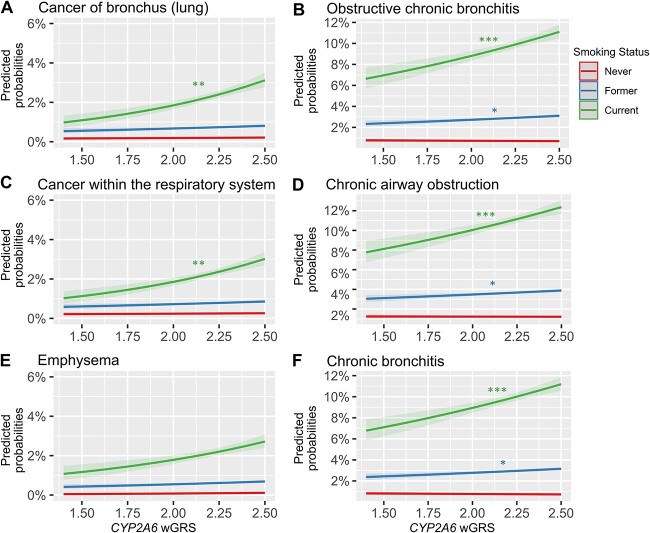
Figure 2.
Smoking modifies the CYP2A6 wGRS effects on disease risk. Smoking status (current, former, versus never smokers) interactions plotted as predicted disease probability with confidence intervals for the six phenome-wide significant signals: (A) cancer of bronchus (lung), (B) obstructive chronic bronchitis, (C) cancer within the respiratory system, (D) chronic airway obstruction, (E) emphysema, and (F) chronic bronchitis. Interaction term significance denoted as P < 0.001 ‘***’, <0.01 ‘**’, <0.05 ‘*’). The never smokers group is the reference. Interaction sample (N = 358 528–394 469); cases and controls sample sizes are found in Supplementary Table 2.