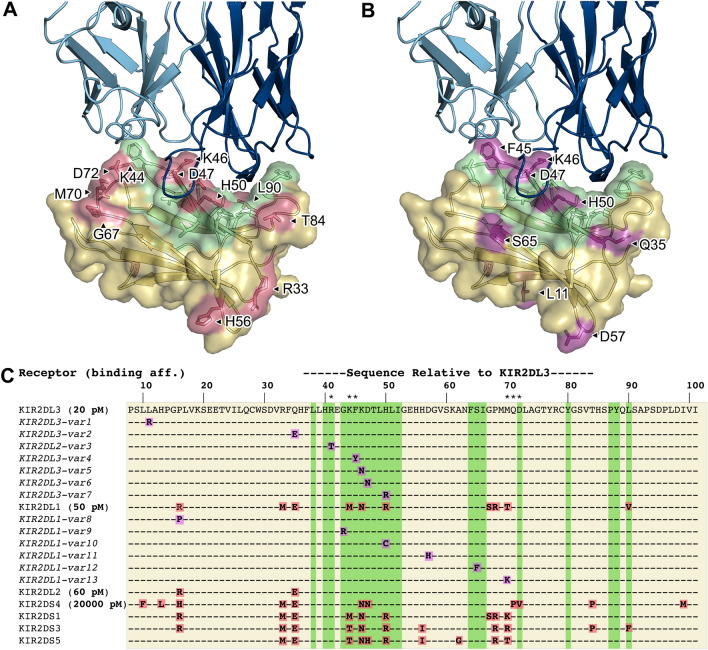
Figure 4.
Polymorphism between KIR2D class receptors and their variants is often part of the lirilumab epitope. (A), (B) Lirilumab-similar binding footprint (green) overlaid with polymorphic sites between KIR2D class receptors (red) and sites of KIR2DL3 and KIR2DL1 variant polymorphisms (magenta). (C) A sequence alignment of KIR2D receptors and variants (from EMBL-EBI IPD-KIR database, release 2.12) that result in amino acid mutations in the KIR domain bound by lirilumab. KIR2DL1 and KIR2DL2 variant mutations are displayed relative to their respective parent receptor sequences, while mutations in all other aligned sequences are relative to KIR2DL3. Sequence numbering corresponds to the KIR2DL3 sequence. Asterisks (*) above the sequence alignment indicate amino acids involved in KIR:HLA binding. Alignment coloring corresponds to the surface colors in panels A and B. Binding affinity constants as previously determined by ELISA (Table 2) are shown in bold font next to the KIR2D receptor name. See Table S2 for variant accession numbers and listing of other high frequency KIR2D variants.