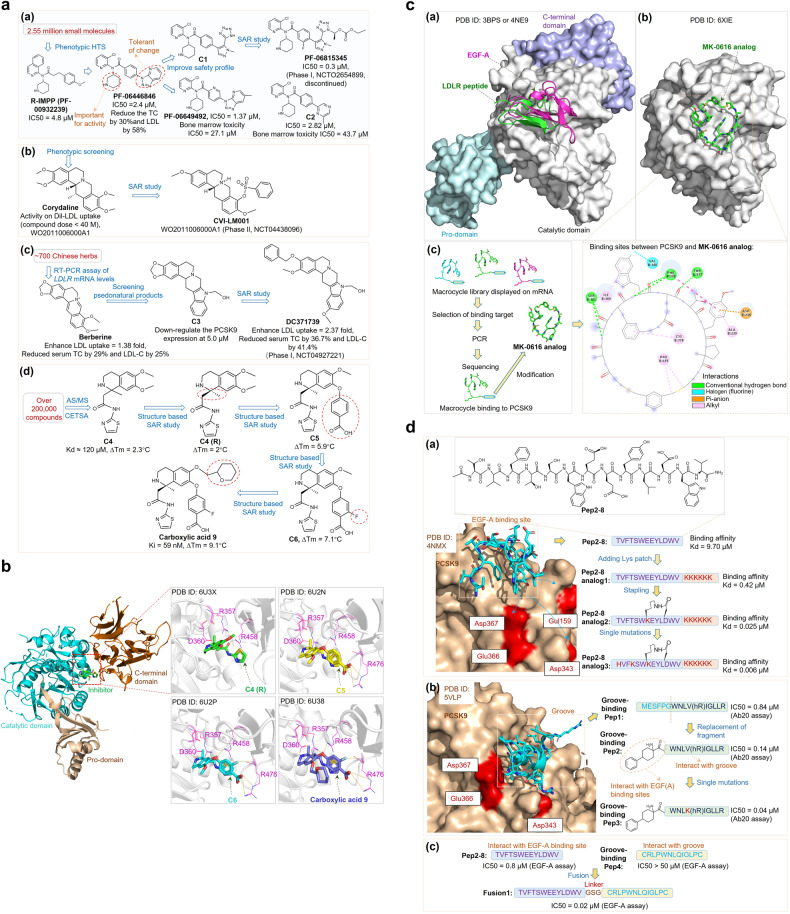
Fig. 5.
The strategies to develop emerging PCSK9 inhibitors. a Strategies for the development of four representative PCSK9 inhibitors: PF-06815345 (a), CVI-LM001 (b), DC371739 (c), and carboxylic acid 9 (d). b The crystal structures of PCSK9 with small-molecule inhibitors. Crystal structures were adapted from https://www.rcsb.org/ (PDB ID: 6U3X, 6U2N, 6U2P, 6U38). c The co-crystal structures of PCSK9 with EGF-A (pink), LDLR peptide (green) (a) or PCSK9 with MK-0616 analog (b), and the strategy of development of macrocyclic PCSK9 inhibitor from mRNA display (c). Crystal structures were adapted from https://www.rcsb.org/ (PDB ID: 3BPS, 4NE9, 6XIE). d The crystal structures of the complex of Pep2–8 (a) and groove-binding Pep1 (b) with PCSK9 and strategies to develop the indicated PCSK9 inhibitors (a-c). Crystal structures were adapted from https://www.rcsb.org/ (PDB ID: 4NMX, 5VLP). AS/MS affinity selection/mass spectrometry, CETSA cellular thermal shift assay, SAR structure-activity relationships, ∆Tm melting temperature shift, Kd dissociation constant, Ki inhibition constant, Ab20 PCSK9-binding antibody 20, EGF-A epidermal growth-factor-like domain A, IC50 half-maximal inhibitory concentration. Panels were illustrated by ChemDraw and Microsoft PowerPoint