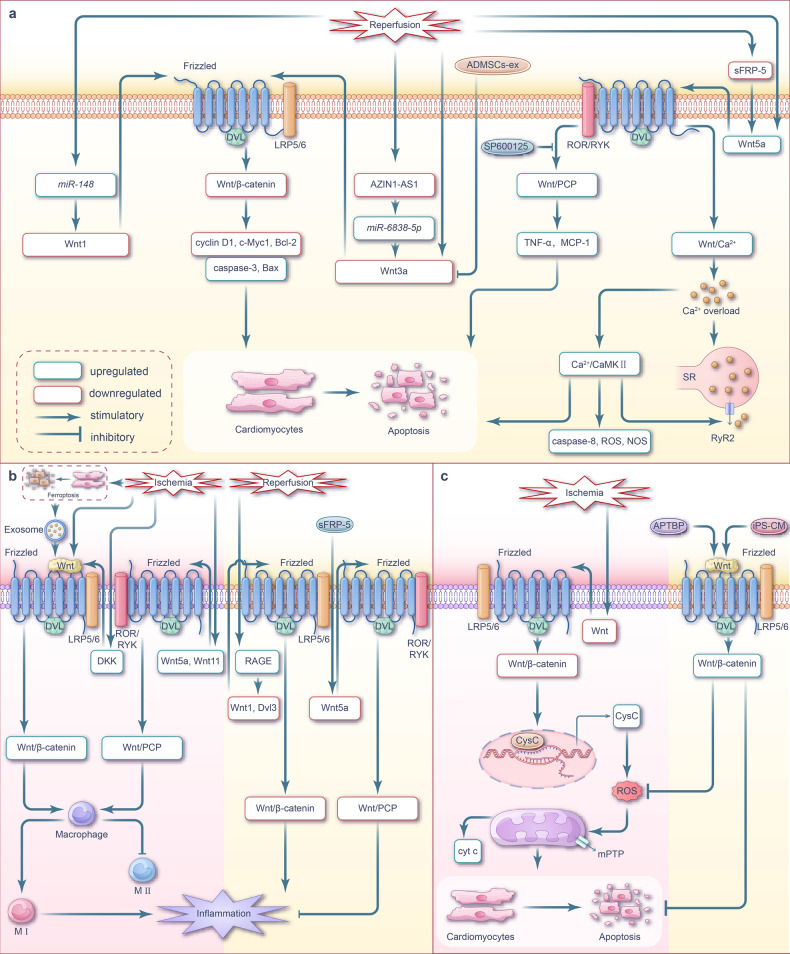
Fig. 2.
Wnt signaling pathway and targeted therapy for apoptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress during myocardial I/R injury. a Wnt signaling pathway-mediated apoptosis during myocardial I/R injury. During myocardial I/R injury, the inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes cardiomyocytes apoptosis. However, the roles of non-canonical Wnt/PCP and Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathways in myocardial I/R injury are the opposite. The activation of these two Wnt signaling pathways may exacerbate cardiomyocyte apoptosis through the activation of the JNK pathway or the induction of calcium overload. b Wnt signaling-mediated inflammation during myocardial I/R injury. Cardiomyocyte ferroptosis occurs during the ischemia phase, and the exosomes derived from the ferroptotic cells induce M1 macrophage transformation by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. During myocardial ischemic phase, the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes the polarization of macrophages towards the M1 phenotype while suppressing the M2 phenotype, ultimately exacerbating the inflammatory response. Upregulation of Wnt ligands and DKK family members in macrophages stimulates inflammation by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. During the process I/R injury, there is an upregulation of RAGE expression in the infarct border zone of rat cardiomyocytes, accompanied by downregulation of Wnt1 and Dvl3 expression. By inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, this leads to the promotion of inflammatory response, exacerbating cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Additionally, activation of the Wnt/PCP pathway in macrophages during the ischemic phase increases the expression of inflammatory cytokines, which aggravates cardiac inflammation. c Wnt signaling-mediated oxidative stress during myocardial I/R injury. During myocardial ischemia phase, the downregulation of Wnt protein inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling transduction, resulting in increased transcription of intracellular CysC. The elevated expression of CysC exacerbates intracellular oxidative stress and promotes the generation of ROS leading to cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Note: The pink background represents the ischemic phase, while the cream background represents the reperfusion phase. ADMSCs-ex exosomes isolated from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells, sFRP-5 secretory frizzled-related protein 5, LRP low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, ROR recombinant receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor, RYK receptor tyrosine kinase, CaMKII calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, ROS reactive oxygen species, NOS nitric oxide synthase, RyR ryanodine receptors, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-α, MCP-1 monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, APTBP a peptide from tuna backbone protein, CysC cystatin C, mPTP mitochondrial permeability transition pore, cyt c cytochrome c, iPS-CM induced plenipotentiary stem cell-derived conditioned medium