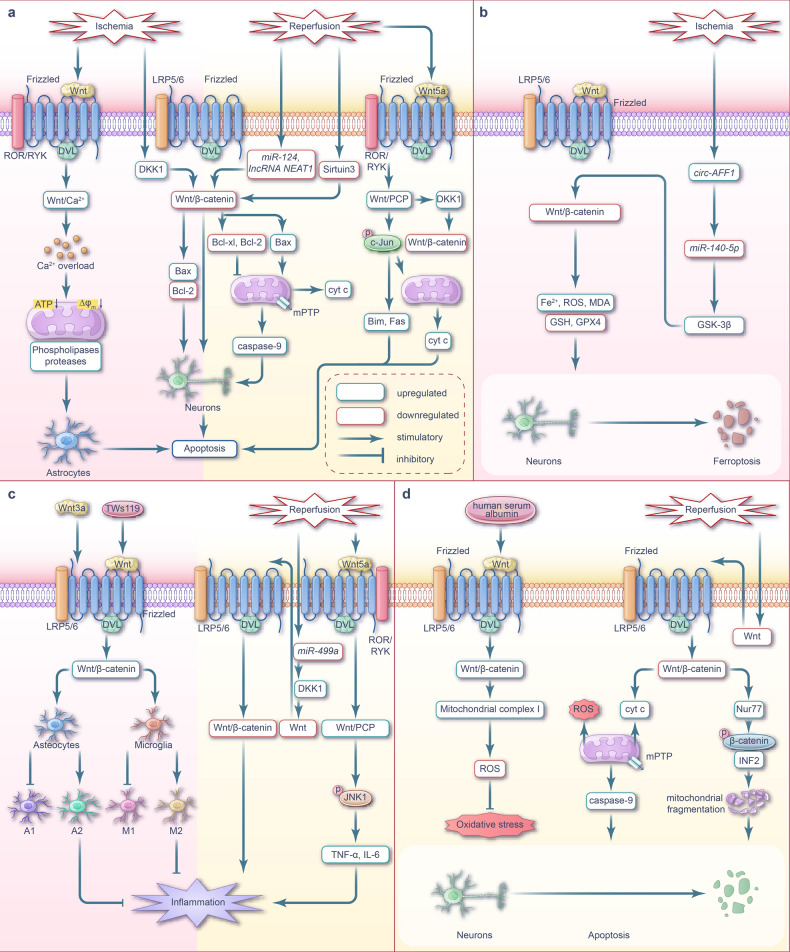
Fig. 4.
Wnt signaling pathway and targeted therapy for apoptosis, ferroptosis, inflammation, and oxidative stress during cerebral I/R injury. a Wnt signaling-mediated apoptosis during cerebral I/R injury. During cerebral ischemic phase, Wnt/Ca2+ signaling is activated, leading to intracellular calcium overload and and subsequent astrocyte apoptosis. The upregulation of DKK1 inhibits Wnt/β-catenin pathway, leading to neuronal apoptosis. During cerebral I/R phase, Wnt5a-mediated Wnt/PCP signaling is activated, promoting c-Jun phosphorylation, inducing cyt c release from mitochondria, inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling, and ultimately leads to neuronal apoptosis. Downregulation of Sirtuin3, miR-124 and lncRNA NEAT1 also inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling. b Wnt signaling-mediated ferroptosis during cerebral I/R injury. During cerebral ischemia phase, circ-AFF1 is highly expressed and directly targets miR-140-5p to upregulate GSK-3β. The highly expressed GSK-3β inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling leads to excessive accumulation of Fe2+, ROS and MDA, and suppression of GSH and GPX4 expression, thereby aggravating neuronal ferroptosis. c Wnt signaling-mediated inflammation during cerebral I/R injury. During cerebral ischemic phase, Wnt/β-catenin signaling is activated, which promotes the polarization of reactive microglia to M2 phenotype, increases the number of A2 type of astrocytes, and reduces the number of A1 type of astrocytes, thereby playing a protective effect and reducing the inflammatory response caused by cerebral ischemia. During cerebral I/R phase, downregulation of miR-499a leads to inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, thereby aggravating the inflammatory response. Wnt5a-mediated Wnt/PCP signaling is activated during cerebral I/R, leading to upregulation of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus aggravates the inflammatory response during cerebral I/R. d Wnt signaling-mediated oxidative stress during cerebral I/R injury. During cerebral I/R phase, Wnt/β-catenin signaling is inhibited which lead to neuronal apoptosis via mitochondria dysfunction. The expression of Nur77 is stimulated in the oxidative stress environment during cerebral I/R, which leads to mitochondrial fragmentation by promoting β-catenin phosphorylation and INF2 expression. Intravenous injection of human serum albumin activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling, thereby increasing mitochondrial complex I activity, reducing ROS generation, suppressing oxidative stress, and playing a therapeutic role during cerebral I/R. Note: The pink background represents the ischemic phase, while the cream background represents the reperfusion phase. LRP low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, ROR recombinant receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor, RYK receptor tyrosine kinase, ATP adenosine triphosphate, Δφ membrane potential, DKK1 Dickkopf-1, cyt c cytochrome-c, GSH glutathione, GPX4 glutathione peroxidase 4, GSK-3β glucogen synthase kinase 3β, JNK1 c-Jun amino-terminal kinase1, TNF-α tumor necrosis factor-α, TWS119 a GSK-3β inhibitor that activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling, Nur77 nuclear hormone receptor NUR/77, INF2 inverted formin 2, mPTP mitochondrial permeability transition pore