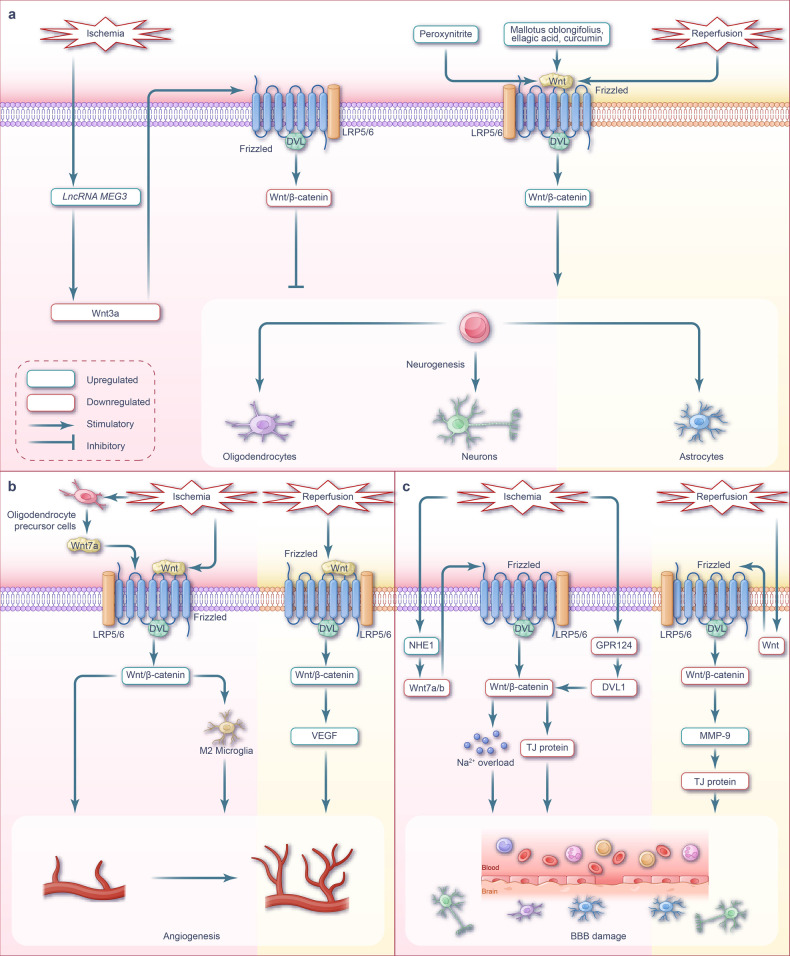
Fig. 5.
Wnt signaling pathway and targeted therapy for neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and BBB during cerebral I/R injury. a Wnt signaling-mediated neurogenesis during cerebral I/R injury. During cerebral ischemia phase, there is an elevation in the synthesis of lncRNA MEG and peroxynitrite. The highly expressed lncRNA MEG hampers the process of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In contrast, increased levels of peroxynitrite activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In the subsequent phase of cerebral I/R phase, the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays a crucial role in promoting neurogenesis. Mallotus oblongifolius, ellagic acid, and curcumin enhance the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling, leading to the promotion of neurogenesis and the exertion of therapeutic effects on cerebral ischemia or I/R injury. b Wnt signaling-mediated angiogenesis during cerebral I/R injury. Following cerebral ischemia, oligodendrocyte precursor cells within the brain secrete Wnt7a, which triggers the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling specifically in endothelial cells. This activation, in turn, facilitates the process of angiogenesis. Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway induces the conversion of microglia into the M2 phenotype, thereby facilitating angiogenesis following an ischemic stroke. Following cerebral I/R, the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway upregulates the expression of VEGF and VEGF receptors. This activation promotes angiogenesis and stimulates the proliferation and sprouting of vascular endothelial cells. c Wnt signaling-mediated the BBB during cerebral I/R injury. The mutation or deletion of GPR124 leads to a reduction in the recruitment of DVL1 to the cell membrane. Consequently, this weakens the transduction of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, resulting in the downregulation of TJ protein expression between microvascular endothelial cells. As a consequence, it exacerbates the damage to the BBB following cerebral ischemia. Moreover, during the cerebral ischemic phase, there is an upregulation of NHE1, which inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disrupts astrocyte function. This disruption is necessary to maintain the integrity of the BBB. In the context of cerebral ischemia, NHE1 undergoes upregulation, which subsequently inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disrupts the function of astrocytes. This disruption ultimately results in impaired BBB integrity. During the cerebral I/R phase, there is inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, leading to an increase in the expression of MMP-9. This elevated MMP-9 expression subsequently degrades the TJ proteins between brain endothelial cells, disrupting the integrity of the BBB. Note: The pink background represents the ischemic phase, while the cream background represents the reperfusion phase. LRP low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, BBB blood-brain barrier, GPR124 G protein-coupled receptor 124, TJ protein tight junction protein, MMP-9 matrix metalloproteinase-9, NHE1 the protein encoded by the Nhe1 gene