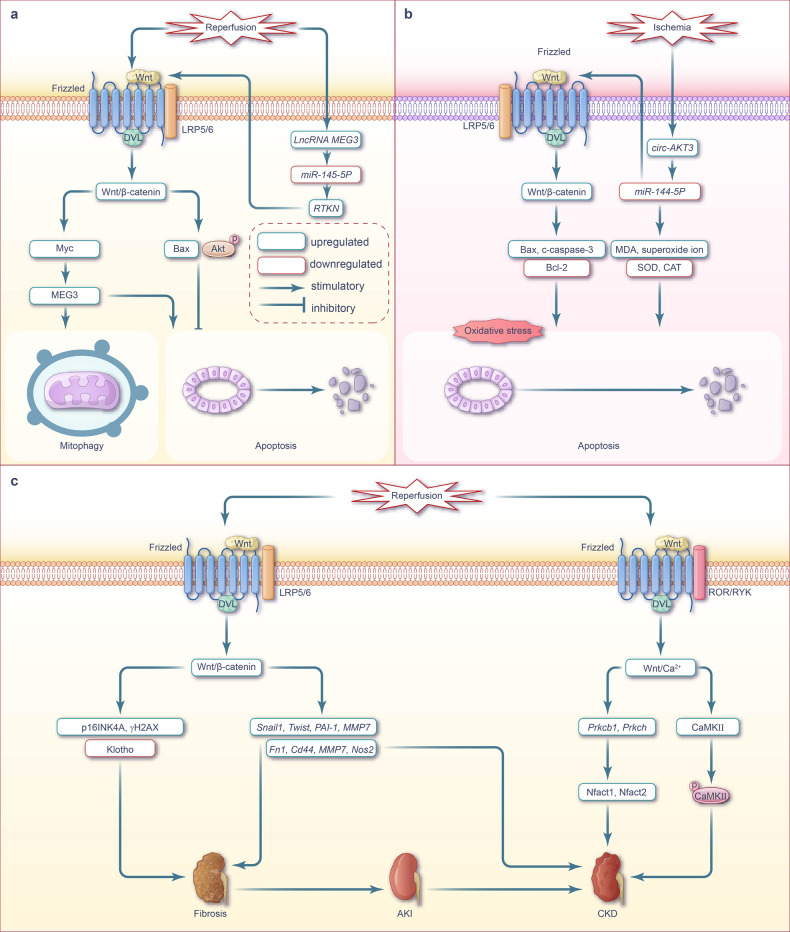
Fig. 6.
Wnt signaling pathway and targeted therapy during renal I/R injury. a Wnt signaling-mediated apoptosis during renal I/R injury. During the renal I/R phase, there is an upregulation of lncRNA MEG3, which leads to the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. This activation, in turn, promotes mitophagy and induces apoptosis in renal cells. b Wnt signaling-mediated oxidative stress during renal I/R injury. In the renal ischemic phase, there is a downregulation of miR-144-5p, which in turn activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. This activation leads to increased oxidative stress and apoptosis in renal cells. Additionally, circ-AKT3 further contributes to the reduction of miR-144-5p expression, thereby exacerbating renal cell apoptosis. c Wnt signaling-mediated cell senescence and renal fibrosis apoptosis during renal I/R injury. During the phase of renal I/R, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is activated, leading to the promotion of renal cell apoptosis and the development of fibrosis. Additionally, the activation of Wnt/Ca2+ signaling during this process contributes to chronic kidney injury. Note: The pink background represents the ischemic phase, while the cream background represents the reperfusion phase. LRP low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, ROR recombinant receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor, RYK receptor tyrosine kinase, MDA malondialdehyde, SOD superoxide dismutase, CAT catalase, CaMKII calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, AKI acute kidney injury, CKD chronic kidney disease