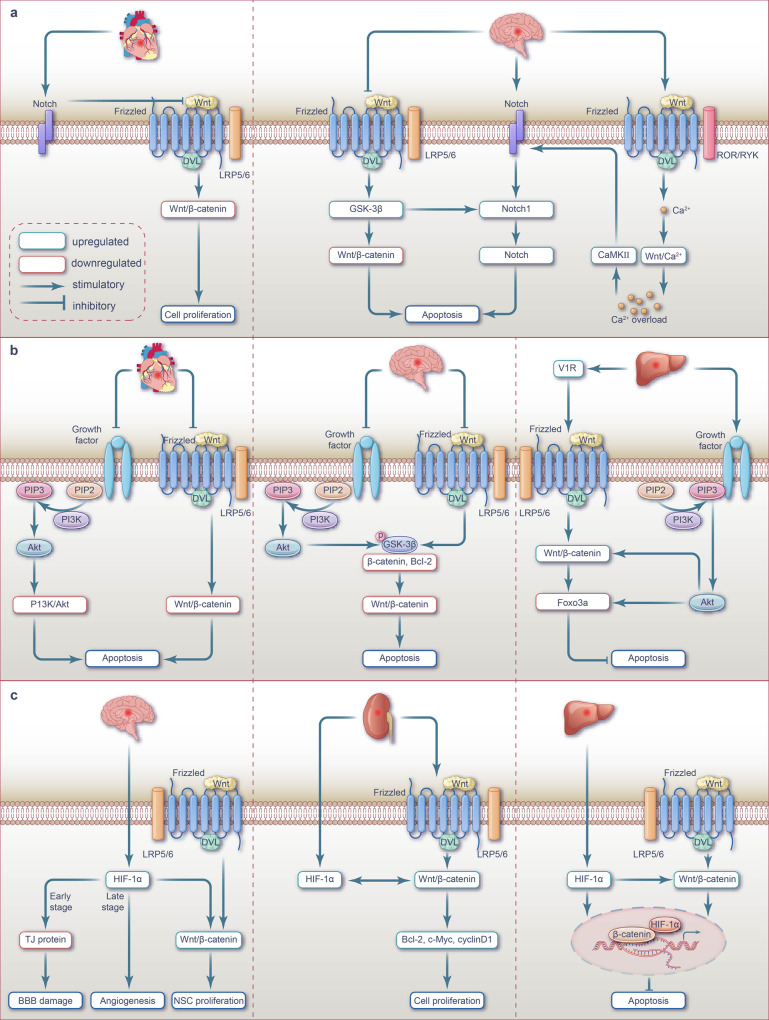
Fig. 8.
Interplay of Wnt, Notch, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways during I/R Injury: Insights from Crosstalk Mechanisms. a Crosstalk between Wnt and Notch signaling pathway during I/R injury. During zebrafish myocardial I/R injury, the activated Notch signaling inhibites the Wnt signaling transduction and restored the proliferation ability of certain cardiomyocytes. In the process of cerebral ischemia phase, Wnt/β-catenin signaling is inhibited while Notch signaling is activated. These two signals crosstalk through GSK-3β to promote apoptosis. Additionally, the Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway is concurrently upregulated, which crosstalks with Notch signaling to enhance the Notch signaling activity. b Crosstalk between Wnt and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway during I/R injury. During myocardial I/R injury, both PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways are downregulated. This downregulation inhibits the crosstalk between these pathways, ultimately resulting in cardiomyocyte apoptosis and left ventricular dysfunction. Similarly, during cerebral I/R injury, both PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signal pathways are downregulated. In this context, these pathways crosstalk through GSK-3β to promote cell apoptosis, thereby contributing to the pathophysiology of cerebral I/R injury. During hepatic I/R injury, the expression of antidiuretic hormone receptor 1 (V1R) in hepatocytes is upregulated. This upregulation plays a protective role by activating Wnt/β-catenin/FoxO3a/Akt pathway, and then conceals apoptosis induced by FoxO3a activation. c Crosstalk between Wnt and HIF-1α signaling pathway during ischemia or I/R injury. In the context of cerebral ischemia and hypoxia, the increased activity of the HIF-1α signaling pathway plays a role in enhancing the proliferation and neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. During the early stages of the pathological process, HIF-1α disrupts TJ proteins, which subsequently leads to an elevated permeability of the BBB. As the pathological process progresses to the later stages, HIF-1α promotes angiogenesis. In the model AKI induced by H/R, the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway has been shown to enhance the protective effect of HIF, Simultaneously, HIF increases the expression of β-catenin and its downstream target genes. This interaction and crosstalk between HIF and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway contribute to early renal repair after AKI. In context of hepatic hypoxia or H/R, HIF-1α has the ability to competitively bind to β-catenin, leading to enhanced HIF-1α signaling transduction. This interaction serves to reduce apoptosis and promote cell survival in hepatic cells. LRP low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, ROR recombinant receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor, RYK receptor tyrosine kinase, CaMKII calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, PI3K/Akt phosphoinositide-3 kinase/protein kinase B, BBB blood-brain barrier, TJ protein tight junction protein, AKI acute kidney injury, I/R ischemia–reperfusion, V1R antidiuretic hormone receptor 1, NSC neural stem cells