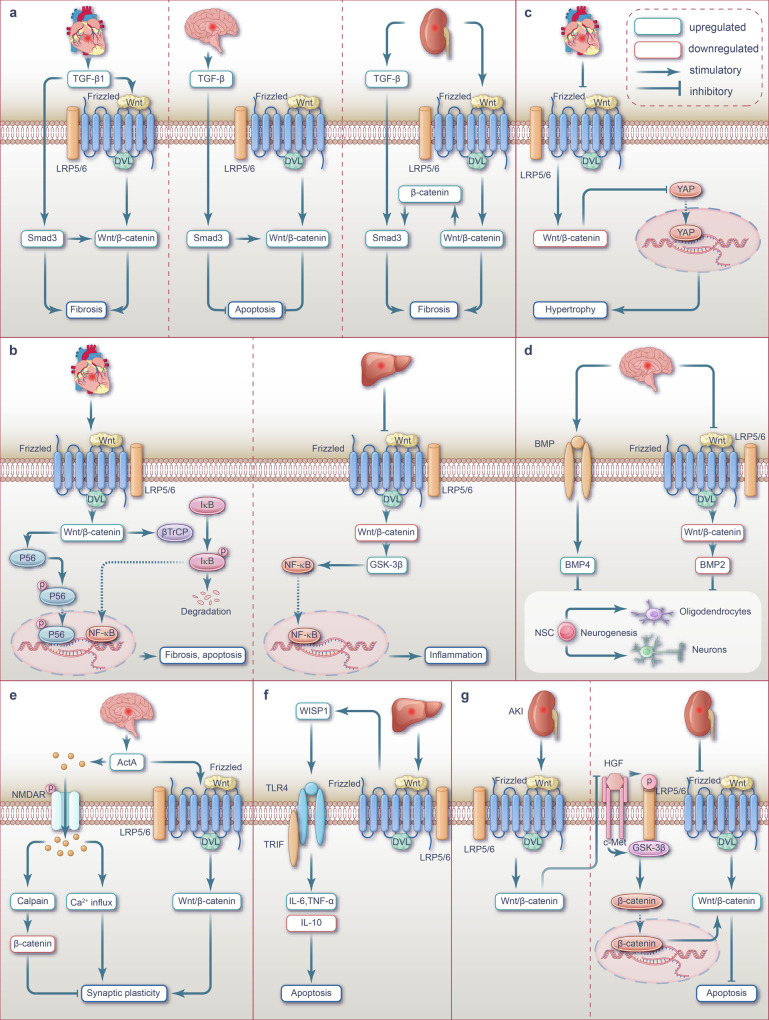
Fig. 9.
Interplay between Wnt, TGF-β, NF-κB, Hippo-YAP, BMP, NMDAR-Ca2+-ActA, TLR4/TRIF and HGF/c-Met signaling pathways during ischemia or I/R injury. a Crosstalk between Wnt and TGF-β signaling pathway during ischemia injury. After myocardial ischemia, there is an increased expression of TGF-β1, which subsequently activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. These two pathways work synergistically to promote the process of myocardial fibrosis. During cerebral ischemia and I/R injury, the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway is activated and collaborates with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to reduce the apoptosis in cortical neuronal caused by cerebral ischemia. Similarly, in renal I/R injury, the TGF-β signaling pathway is activated and interacts with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, contributing to the progression of fibrosis. During this process, β-catenin functions as a transcription cofactor of Smad3, promoting the transcription of downstream target genes and facilitating EMT. b Crosstalk between Wnt and NF-κB signaling pathway during ischemia or I/R injury. During myocardial ischemia, the upregulated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway facilitates the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway by promoting nuclear translocation of p65, this activation induces the migration of cardiac fibroblasts. Additionally, the activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes the degradation of phosphorylated IκB mediated through β-TrCP, subsequently promoting the nuclear translocation of NF-κB, leading to myocardial fibrosis and apoptosis. In contrast, In the process of liver I/R injury, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is inhibited, while NF-κB signaling pathway is activated. The transcription of NF-κB is positively regulated by GSK-3β, which promoted inflammation. the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is inhibited, while the NF-κB signaling pathway is activated. The nuclear translocation of NF-κB is positively regulated by GSK-3β, thereby promoting inflammation. c Crosstalk between Wnt and Hippo-YAP signaling pathway during I/R injury. Following myocardial I/R injury, the Wnt/β-catenin signaling is downregulated, leading to the inhibition of YAP1 transcription. Consequently, the activity of the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway is suppressed. This cooperative effect between the two signaling pathways contributes to the promotion of myocardial hypertrophy. d Crosstalk between Wnt and BMP signaling pathway during ischemia injury. During cerebral hypoxia, there is an upregulation in the expression of BMP4, while the Wnt/β-catenin signaling is inhibited. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin downregulates BMP2 protein expression; thus, the suppressed Wnt/β-catenin signaling and BMP signaling synergistically inhibit the differentiation of neural stem cells into neurons and oligodendrocytes, thereby aggravating cerebral ischemic injury. e Crosstalk between Wnt and NMDAR-Ca2+-ActA signaling pathway during I/R injury. During cerebral ischemia, ActA expression is upregulated, which leads to the Ca2+ influx during synaptic transmission and can also activate the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, synergistically regulating synaptic plasticity. However, Ca2+ influx mediated by NMDAR activation can also trigger the activation of calpain. This activation of calpain subsequently induces cleavage of β-catenin, resulting in a decrease in synaptic stability. f Crosstalk between Wnt and TLR4/TRIF signaling pathway during I/R injury. During hepatic I/R injury, upregulated WISP1 expression activates the TLR4/TRIF signaling pathway, promoting liver injury. g Crosstalk between Wnt and HGF/c-Met signaling pathway during I/R injury. During renal I/R injury, activated HGF promotes the phosphorylation of LRP5/6 and plays an anti-apoptotic effect by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. AKI induces an elevation in Wnt protein levels within renal tubular epithelial cells, consequently activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. The activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibits the secretion of HGF and HGF/c-Met in renal interstitial fibroblasts. Through this coordinated regulation, both the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and the HGF/c-Met signaling pathway play a role in the modulation of apoptosis processes in the context of AKI. LRP low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein, TGF-β transforming growth factor-β, NF-κB nuclear factor-κB, YAP Yes-associated protein, TLR Toll-like receptor, HGF/c-Met hepatocyte growth factor receptor/mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor, BMP bone morphogenetic protein, NMDAR N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor, ActA Activin A; I/R ischemia–reperfusion