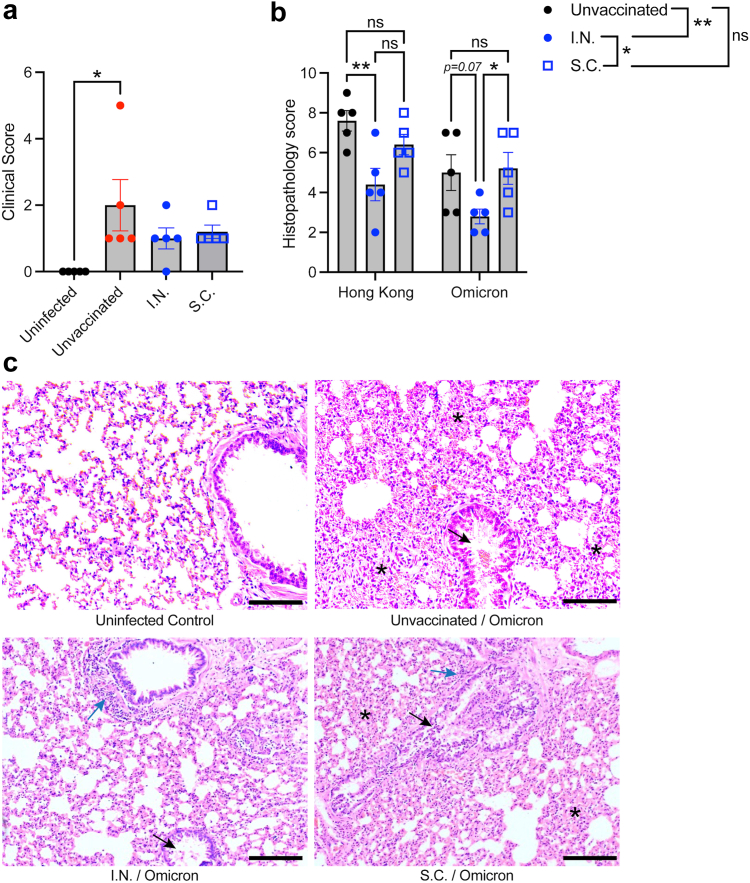
Fig. 7.
Improved lung histopathological scores for I.N. vaccinated hamsters during a heterologous challenge with Omicron. Groups of vaccinated and unvaccinated hamsters (n = 5) were challenged with 105 PFU of Omicron VOC (USA/PHC658/2021). (a) Elevated clinical scores day 4 post-Omicron challenge in unvaccinated animals compared to uninfected controls. ∗p < 0.05 by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. (b) Comparison of histopathological scores for Hong Kong (parental strain, Hong Kong/VM20001061/2020) and Omicron-challenged hamsters. Data from Hong Kong challenged hamsters is re-presented from Fig. 2 to aid comparison. Comparisons of individual vaccine groups for each challenge are indicated on the graphs and comparisons of the influence of vaccination group, independent of the virus challenge strain, are indicated on the figure legend. ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗p < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. The virus strain accounted for 19.7% (p = 0.0034) of the variation in the data, while 33.5% of the variation was accounted for by the vaccination group (p = 0.0012). (c) Representative images of lung tissue from Omicron-infected hamsters, day 4 post-infection. Scale bar = 100 μm. Black arrows indicate examples of bronchiolar epithelial cell death and desquamation, although very mild in the I.N. group. Blue arrows indicate examples peribronchiolar cellular infiltration. Asterisks are placed to indicate examples of pronounced alveolar septal infiltration.