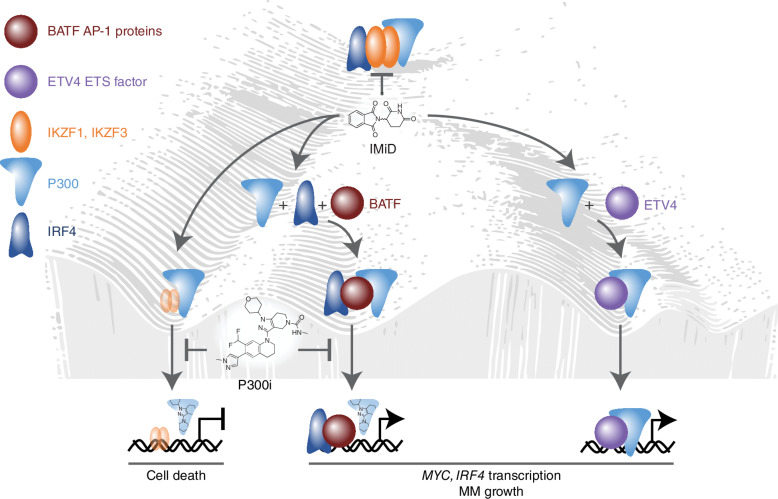
Figure 1.
Transcriptional plasticity sustains SE activities that drive MYC-IRF4-dependent IMiD resistance in multiple myeloma (MM). IMiDs induce multiple myeloma cell death by promoting CRBN-mediated downregulation of IKZF1/IKZF3 and subsequent downregulation of MYC and IRF4 transcription. In IMiD-resistant multiple myeloma cells, IKZF1/IKZF3 dependence of MYC and IRF4 transcription is circumvented via transcriptional plasticity that involves the induction of ETV4 and BATF transcription factors, which bind and recruit p300 to MYC and IRF4 super-enhancers. Accordingly, p300i potentiates the efficacy of IMiDs by downregulating IRF4 and MYC transcription in IMiD-resistant multiple myeloma cells. Figure concept and design by Ben Barwick.