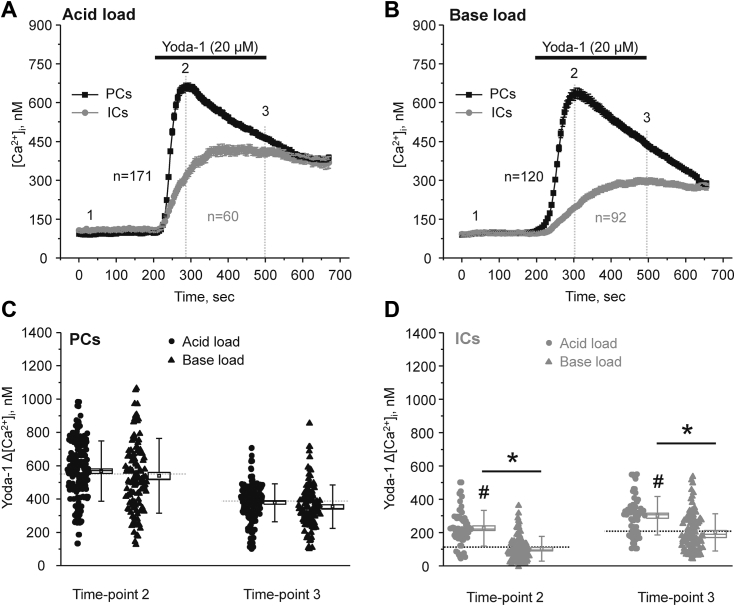
Figure 10.
Metabolic acidosis stimulates Yoda-1-induced [Ca2+]iresponses in the collecting duct intercalated cells.A, the averaged time-courses of [Ca2+]i changes upon application of a selective Piezo1 agonist, 20 μM Yoda-1 (shown with the black bar on top) in individual principal (PCs, black) and intercalated (ICs, gray) cells within split-opened area of the collecting ducts isolated from mice kept on ammonium (NH4Cl, 280 mM) water for three days prior to experiments to induce metabolic acidosis (acid load). Number of individual cells is shown. Six different collecting ducts from three different mice were used for analysis. B, the averaged time-courses of [Ca2+]i changes upon application of a selective Piezo1 agonist, 20 μM Yoda-1 (shown with the black bar on top) in individual principal (PCs, black) and intercalated (ICs, gray) cells within split-opened area of the collecting ducts isolated from mice kept on bicarbonate (NaHCO3, 280 mM) water for three days to induce metabolic alkalosis (base load). Number of individual cells is shown. Five different collecting ducts from three different mice were used for analysis. The summary graphs comparing the magnitudes of Yoda-1-mediated [Ca2+]i elevations calculated as the difference in [Ca2+]i values before (time point 1), at the beginning (time point 2), and at the end (time point 3) of Yoda-1 application in individual PCs (C) and ICs (D) from the conditions in (A and B). Bars and whiskers represent SE and SD, respectively. Mean and median values are denoted with a dot and a line, respectively. Dashed lines represent respective average values in control (untreated) conditions. ∗- significant decrease (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test) between experimental groups shown with lines on the top. # - significant increase (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test) versus respective control values shown in Figure 2C. ICs, intercalated cells; PCs, principal cells.